
DOI: Bureau of Land Management
Att: Director (630); 1004-AE92
1849 C St NW, Room 5646
Washington DC 20240
RE: Conservation and Landscape Health Proposal
Docket # 1004-AE-92
Dear Sirs:
Please accept these comments as the vigorous opposition of the above-named Organizations with regard to the Conservation and Landscape Health Proposal Docket #1004-AE-92 (“The Proposal”). Our Organizations represent a broad spectrum of motorized recreational interests from snowmobiling to four-wheel drive vehicles, ATVs, UTVs, motorcycles and more. The Organizations are concerned that the Proposal appears to be more of a jumbled planning wish list to benefit conservation interests than a coherent revision to planning efforts that aligns with multiple uses. While our motorized recreational interests have been the subject of more than 50 years of NEPA analysis and planning to protect resources, this effort is not addressed at all in the Proposal. We are opposing to any trail loss resulting from conservation leases, ACEC expansions or other efforts that do not recognize the decades of analysis already in place on these routes and areas.
Executive Summary.
The Organizations comments are as comprehensive as possible and include responses to specific sections of the BLM rulemaking and more systemic concerns not specifically addressed in the Proposal. The Organizations are not entirely opposed to monetizing the method of conservation, however we are skeptical about the corresponding value of the effort and very concerned about the corresponding threat that is posed to other legitimate land uses. As will be discussed in greater detail below the United Nations, through the UN Environment Programm- World Conservation Monitoring Centre (UNEP-WCMC) has provided significant guidance on the role of governments in creating conservation credits, how to equitably allocate credits and avoid other pitfalls through the issuance of high-quality analysis and planning documents. None of this guidance or issues identified in the guidance are addressed meaningfully in the Proposal but rather the Proposal falls into every pitfall warned against by the UN.
It is important to note that the motorized trails community as through our voluntary registration programs developed with various states, has provided between $200-300 million a year for the management of recreational opportunities and resource protection across the country for decades. Off-Highway Vehicle and Over the Snow Vehicle manufacturers provide hundreds of millions of dollars in additional project specific funding for efforts on public lands, and we are sure would also like to discuss how marketable credits could be obtained to expand the impact and benefit of these programs.[1] A significant portion of these projects could be the basis for the motorized community to obtain access to conservation credits. Given our decades of working partnerships with public land managers, the Organizations believed this would have warranted some type of discussion with public lands managers. Apparently, it did not. We contend the Proposal should address participation in the allocation of conservation credits by all interests engaged in conservation including the motorized recreational motorized community.
While the motorized trails community certainly is player in these efforts already, the Organizations are frustrated by the methodology adopted throughout the Proposal, which appears to avoid any meaningful discussion of issues. Foundational questions such as the following simply are not addressed. Question 1. What statutory basis is relied on for many of the provisions? Question 2. Is a lease the proper tool to be used to create conservation credits? What are other manners to allocate credits? Question 3. Who are the entities working with BLM on conservation efforts, and who might be interested in capturing credits for those existing efforts? Question 4. What is the relationship between ACEC processes proposed to be expanded and conservation lease creation? Question 5. What are the perceived deficiencies in the current ACEC processes? Question 6. How do any of these concepts relate to multiple uses and existing efforts? Basic information, such as statutes supporting a concept or idea would be highly valuable to the public in analyzing questions like this, as it would enable stakeholders to infer some type of structure to the effort.
The Organizations vigorously assert that generalized conservation leasing cannot be a vehicle or tool that would lead to the loss of multiple uses in any area temporarily or more permanently by mandating a particular management prescription. In our previous experiences, mission creep of previous conservation efforts has led to unresolvable challenges more than 50 years after areas were inventoried for conservation possibilities. If safeguards against this type of management creep cannot be provided this is a major concern. In fact, the issue extends beyond conservation leases as it has been our experience that ACEC proposals from the public are commonly submitted in the RMP development process. These Proposals often encompass large portions of a planning area, rendering any assertion of the ACEC standard not being applied in planning, factually problematic. It has been our experience that many of these citizen inventories lack factual accuracy on the ground such as proposing to designate areas for protection that have already been found unsuitable for protection for the same reasons in other efforts. This commonly found with critical habitat for ESA species. We would support efforts to update BLM planning documents, but these efforts must comply with planning regulations. The Proposal fails to provide any input on issues such as this.
Even when questions are addressed, the information falls well of providing anything of substantive value. Rather than meaningfully addressing foundational questions such as “Would the Proposal would create a carbon offset lease or a conservation lease?” This basic issue is relegated to one line in a 22-page Proposal. These are two entirely different concepts and should be clearly addressed in the Proposal as these distinctions are going to be critical. Creating a common starting point for discussion and analysis is critical as every interest will be approaching large scale planning with significantly different levels of technical expertise and understanding of the Proposal’s various components. A commonly understood starting point is essential for success.
Another example of how the Proposal avoids meaningful discussion and input from partners is provided in the woefully inadequate Economic Analysis, which asserts that there will not be a significant economic impact to communities or the BLM from the Proposal. If this is accurate, why would the Proposal be brought forward? It is our understanding that the Proposal seeks to develop an entirely new revenue stream for conservation on public lands and this is a major economic benefit that warrants analysis and meaningful discussion. We have no idea why this type of discussion would be avoided. Understanding the scale of new resources would be a major tool in creating public support for the process and effort and success in the long term.
These types of failures of analysis continue far beyond these cited examples and cumulatively create a Proposal that is very difficult to comment on in a substantive and meaningful manner. Rather than collaboratively working with existing partners and interests to determine the best method for implementation of a conservation credit capture system, that could benefit everyone who has partnered with public lands managers for decades, the Proposal simply starts from a position that large scale leases are the best tool for creation of conservation credits. We are also concerned that a poorly defined credit program will create immense mistrust between managers and existing partners and eventually be struck down as legally insufficient.
The Organizations are also concerned that the Proposal fails to recognize the fact that BLM is significantly short staffed in most areas and is working with many Resource Management Plans that are more than 40 years old. Even recently updated RMPs do not have any analysis of areas that might be highly suited to development of conservation credit programs. Rather than addressing these basic issues to develop a balanced and effective model on the ground, the Proposal fails to recognize the huge new layers of data and analysis to be addressed in the planning process. Generally, there needs to be significantly more information provided on the various resources to be applied and how these various resources will be targeted to issues and this will result in an immense new planning burden on offices that are already short staffed. Our concern is many of these offices have projects moving that we have funded and would like to see completed and these should not be stopped to accommodate a new national planning process. The Organizations vigorously assert that no current public access should be lost after these opportunities have been through more than 50 years of highly detailed NEPA analysis and found sustainable after site specific Environmental Assessment or Environmental Impact Statements. No current or future site specific NEPA efforts should be delayed to implement the Proposal that is be supported by a categorical exclusion that is to be created at some point in the future.
1(a)(1) Who we are.
Prior to addressing the specific input of the Organizations on the Proposal, we believe a brief summary of each Organization is needed. The Colorado Off-Highway Vehicle Coalition (“COHVCO”) is a grassroots advocacy organization representing the OHV community seeking to represent, assist, educate, and empower all OHV recreationists in the protection and promotion of off-highway motorized recreation throughout Colorado. COHVCO is an environmental organization that advocates and promotes the responsible use and conservation of our public lands and natural resources to preserve their aesthetic and recreational qualities for future generations. The TPA is an advocacy organization created to be a viable partner to public lands managers, working with the United States Forest Service (USFS) and the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) to preserve the sport of motorized trail riding and multiple-use recreation. The TPA acts as an advocate for the sport and takes the necessary action to ensure that the USFS and BLM allocate a fair and equitable percentage of public lands access to diverse multiple-use trail recreational opportunities. Colorado Snowmobile Association (“CSA”) was founded in 1970 to unite winter motorized recreationists across the state to enjoy their passion. CSA has also become the voice of organized snowmobiling seeking to advance, promote and preserve the sport of snowmobiling through work with Federal and state land management agencies and local, state and federal legislators telling the truth about our sport. CORE is a motorized action group dedicated to keeping motorized trails open in Central Colorado and the region. Idaho Recreation Council (“IRC”) is comprised of Idahoans from all parts of the state with a wide spectrum of recreational interests and a love for the future of Idaho and a desire to preserve recreation for future generations. The Idaho State Snowmobile Association (“ISSA”)is an organization dedicated to preserving, protecting, and promoting snowmobiling in the great state of Idaho. Our members may come from every corner of the state, but they all share one thing in common: their love for snowmobiling. Ride with Respect (“RwR”) was founded in 2002 to conserve shared-use trails and their surroundings. RwR has educated visitors and performed over twenty-thousand hours of high-quality trail work on public lands most of which has occurred on BLM lands. Over 750 individuals have contributed money or volunteered time to the organization. The Alaska Snowmachine Alliance(“ASA”) supports snowmachining throughout the State of Alaska and all snowmachine activities including racing and vintage, snowmachine trails, the SnowTRAC program and it’s funding, snowmachine Search and Rescue and the betterment of snowmachining throughout the State of Alaska. Nevada Off Road Association (NVORA) is a non-profit Corporation created for and by offroad riders. NVORA was formed to specifically fill the void between the government managers and the rest of us who actively recreate in the Silver State. NVORA does this by maintaining a consistent, durable, and respected relationship with all stakeholders while facilitating a cooperative environment amongst our community. Collectively, TPA, NORA, CSA, CORE, IRC, RwR, ISSA, ASA and COHVCO will be referred to as “The Organizations” for purposes of these comments.
1(a)(2). BLM has benefited from decades of successful partnerships with the motorized community.
An important component of any successful planning effort and conservation project has always been the recognition of the history of the management issue and previous successes in the area. The Organizations are intimately aware of the challenges in managing healthy public lands and the exceptionally limited resources that the agency has available. The Organizations must also recognize that these voluntary state registration programs are actually implementing the full range of goals and objectives identified in multiple use statutes and as identified in EO 14008 and EO 14072 issued by President Biden. As a result of these efforts, recreational opportunities are improved, economic benefits to local communities area expanded and resources are protected for the future. As discussed in more detail subsequently, we are concerned these mandates are not provided for in the Proposal.
Nationally, the OHV community provides between $200-$300 million dollars into public lands management every year as a result of their voluntarily created OHV/OSV registration programs. As an example, the California OHV grant program provided $85 million in grants last year, and over the life of the program has funded more than $750 million in direct funding to public land managers.[2] The benefits of the California OHV program are outlined as follows:
- Through our USFS partners, over 18,000 miles and 269,000 acres are available for OHV Recreation.
- Through our BLM partners, over 18,000 miles and 478,000 of acres are made available for OHV Recreation.
Clearly efforts at the scale of these voluntarily created programs warrant inclusion in the discussion of conservation credits. As another example, Colorado’s voluntary registration programs put almost $9m annually in grants back on public lands, and over the life of this program this has now provided more than $100m in funding for public lands to maintain and protect all forms of resources.[3] This Program funds more than 60 maintenance crews throughout the state in addition to equipping and often training them to. Most states that BLM owns lands in have similar programs that provide similarly high levels of funding but these programs extend well beyond just federal public lands and many states have OHV/OSV programs but have little to no federal public lands.
Understanding this partnership and its benefits for recreation and conservation would have avoided erroneous statements in the Proposal, such as assertions that recreation is a landscape level threat to public lands, closures for the benefit of conservation and assertions that conservation leases should result in subsequent conservation management standards. Recognition of the benefits of multiple use restoration efforts in protecting the future of multiple uses in the area could have been highly valuable, but was not even mentioned in the Proposal.
While portions of these funds from voluntary registration programs are used in manners that may not be the basis for a conservation credit, many of the projects are efforts that could generate conservation or carbon credits from efforts directly occurring on the ground. As an example, the Colorado OHV program has contributed more than $1m over the last several years to repair the impacts of the East Troublesome fire which impacted more than 190k acres largely on BLM’s Kremmling FO and Arapahoe/Roosevelt NF. Initial efforts targeted restoring basic access to the area to allow restoration efforts to even start and we anticipate planting a large number of seedlings and monitoring the area to conclude these efforts.[4] This is a type of project that commonly occurs within our OHV/OSV programs and would clearly be a project that could generate both carbon and conservation credits throughout. These are the type of projects we would be concerned about slowing down if there was a leasing component that would need to be complied with to create or capture credits from the project. Why would a partnership such as this not be highlighted and targeted for future planning efforts?
The efforts of the motorized community extend well beyond landscape level efforts and often are targeting much smaller scale areas on an on-going basis. Many of our local volunteer clubs work with land managers have executed “adopt a trail” or “adopt a road” type agreement for large portions of routes in planning areas. These clubs often partner with managers on very small acre projects and efforts to address impacts of illegal shooting or dumping in areas with clean up days. These efforts have been highly effective in mitigating impacts of illegal activities. The picture below represents one clubs single day efforts cleaning up an illegal dumping site on BLM lands in partnership with managers.
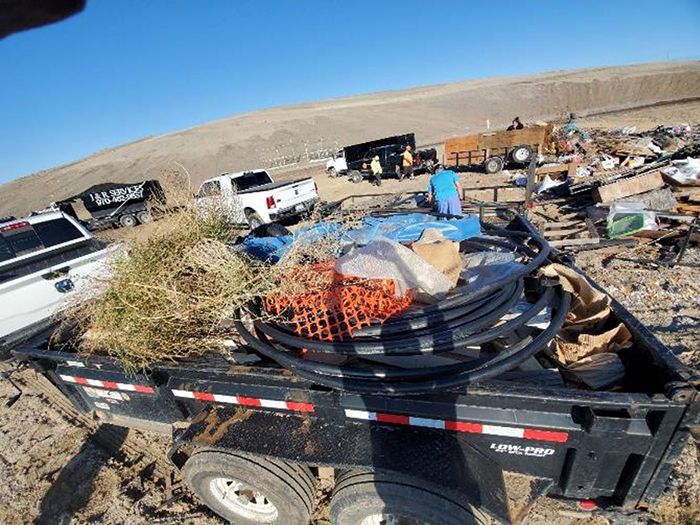

The Proposal provides no discussion at all on how efforts such as this would be addressed if these areas were also subject to a conservation lease. How would this be recognized and unnecessary impacts to these programs be avoided? The Organizations believe it is critical to note that all these efforts are occurring within the scope of existing BLM regulations. This situation forces us to ask why there would be any desire to provide leases and other tools for these efforts, when existing resources can do the work that is sought to be done with conservation leases? This conflict raises a concern that maybe the asserted goals and objectives of the Proposal are not well aligned with the actual discussions occurring as issues with existing efforts would have been immediately apparent.
2(a) Recreation is a landscape level threat to public lands?
The Proposal adopts a model of analysis that fails to recognize existing contributions or partners already working in the conservation space, and address how efforts would be incorporated in the development of the conservation credit program and any new planning efforts. The Organizations hope this is the result of urgency to implement the Program but this urgency in development of the Proposal has led to landscape level conclusions in the Proposal that are factually problematic and could be barriers to the implementation of a program moving forward and its long-term success.
One such example of a factually problematic conclusion that will not speed implementation of the Proposal is the determination that recreation poses a landscape scale threat to public lands which is outlined as follows:
“The BLM implements this mandate through land use plan designations, allocations, and other planning decisions that conserve public land resources and seek to balance conservation use with other uses such as energy development and recreation. The BLM also implements this mandate in other decision making and management actions by promoting conservation use, limiting subsequent authorizations when incompatible with conservation use, and mitigating impacts to natural resources on public lands.”[5]
This conclusion is not only shocking but also highly frustrating to partners in the recreational community who has worked with the BLM for decades on a wide range of projects. While the Organizations are aware that recreational impacts might be heightened to a level that is impacting an area at the local level, any assertion that these impacts are occurring at a landscape level is factually challenging at best. Assertions such as this will create significant conflict with existing partners when implementation of the Proposal is attempted.
The Organizations are also very concerned that other foundational positions for the entire Proposal are only questionably accurate and highly conclusory in nature, such as the following provision:
“Ensuring resilient ecosystems has become imperative, as public lands are increasingly degraded and fragmented due to adverse impacts from climate change and a significant increase in authorized use.”[6]
The Organizations would note that the reports cited in the Proposal to support these conclusions were not the basis of significant scholarly review during their development and have not been the subject of public comment until now. Public comment on these reports is not aided by the fact the Proposal does not consolidate these area specific reports into a national report related to the effort. The public is then left to theorize how these various documents and management models will be coordinated after learning of these underlying reports in the Proposal comment period. Any assertion of sufficient time being provided to review the Proposal and the previously unreleased documents would be tricky to defend.
The limited number of scholarly reviews of these foundational reports appear to call the conclusions of this management model into question and recommend a basic course of action other than what the agency is now currently proposing, despite the implementation or subsequent utilization of these reports being unclear. Several journals were released specifically addressing issues and concerns in the accuracy of the reports.[7] We must believe that these reviews would be much larger scale and narrower in scope after the Proposal provides context on the usage of these reports. A sampling of the reviews is problematic for the basic direction of the Proposal as one reviewer summarized the relationship of natural forces and management ability to perform work as follows:
“The emergy input and output of ten ecosystems demonstrate pronounced differences under the same environmental conditions in one county in the agro-pastoral ecotone in China. This analysis enables us to understand the development of ecosystems under anthropogenic influences. Natural resource emergy input is the basic power to maintain ecosystems; purchased emergy input is the direct cause of the development of the ecosystems under the same environmental conditions….how to make policy decisions and use rare natural resources impartially, correctly, and in a well-planned manner will be critical issues in the future for protecting the ecological environment and for the safety of food production” [8]
Other European Union researchers outlined their concerns around an ambiguous and vague foundational planning position creating significant problems when implementing planning decisions as follows:
“The timing in clarifying and operationalize ecosystem services classification and measurements has never been more critical. As ecosystem services become integrated into policy instruments, the need to standardize definitions is essential for monitoring and comparing policy outcomes following different scales of investment (Bennett et al., 2015; Guerry et al., 2015). Our intention in this article is to provide some clarity to address issues related to ecosystem services definition and conceptualization highlighted by others(Boyd and Banzaf, 2007; Fisher and Turner, 2008; Fisher et al.,2009; Wallace, 2007).”[9]
The direct overlap between the recommendations of EU researchers to avoid problems in planning and the problems that are systemic in this Proposal simply cannot be overlooked. The Organizations are familiar with the critical need for accurate analysis in defining the success or failure of the planning effort subsequently and conclusions such as recreation is a landscape level threat is factually problematic. This is also tricky as a starting point for any planning effort.
The ramifications of the Proposal’s factually problematic starting position expands when the decades of governmental efforts towards conservation are addressed. Including the passage of time into the discussion causes the factual accuracy of any assertion to collapse as BLM has managed lands for decades for conservation. Many of these conservation efforts have only resulted from Congressional action after the initial management of lands by BLM. When BLM started managing lands there were no conservation type statutes even in existence. Over the life of the BLM, numerous designations explicitly limit the scope and scale of activity on large portions of federal lands, such as Congressionally designated Wilderness areas, Roadless and Wilderness Study Areas, and other designations generally within the NLCS program make any assertion of landscape level impacts from recreation even more factually problematic. Given that BLM management efforts commenced decades before any of these legislative efforts occurred, we must ask what timeframe was used to come to these determinations? Not only is such a conclusion lacking entirely factual accuracy, it is overly inflammatory to those in the recreational community, and overly inflammatory assertions such as this will prove to be problematic during implementation of the Proposal and undermine any possibility of long-term success.
2(b). Basic information on what the scope and applicability of the Proposal are simply never provided.
Concerns around the foundation for the Proposal extend beyond basic planning assumptions and conclusions, as the Proposal fails to provide any meaningful information or basic clarity on the basic direction of the Proposal. The entry of the federal government into a market seeking to create conservation/carbon offset credits is far more than a conservation leasing program. Foundational issues and questions like “Why wouldn’t the federal government manage this type of a program internally and capture a larger portion of the profits from these credits?” are simply never addressed. These types of questions are far too removed for comments such as these or a few pages in the Federal Register. While many questions about the role of the federal government in the creation of a carbon credit market are far too large for these comments, there are many questions that are highly relevant to partners that basically are never addressed as well.
When the BLM was formed in 1946, concepts and requirements such as Wilderness, Wild and Scenic Rivers, the Endangered Species Act, Multiple Use Sustained Yield Act and Federal Lands Policy and Management Act and the wide range of Congressional protections for resources were still more than 20 years in the future. Any assertion that these landscape level changes entirely for resource protection and conservation have not been major successes in achieving these goals is problematic both factually and legally. Understanding how these existing designations will be integrated into a conservation credit process or expanded ACEC designation process is a basic need. Will efforts in these designations receive a higher level of credits or the same? How will expanded costs of working in these areas be addressed? These are basic pieces of information that should be provided for the motorized community as many of our efforts should be worthy of credit awards already.
The multiple use mandate is clearly defined in the statute and has been refined by thousands of court cases since the passage of these pieces of legislation. Overall, the requirements of multiple use statutory requirements and the general scientific requirements for planning for conservation credits are highly similar in terms of scope and standards. The Organizations assert aligning the Proposal with the legal foundation is problematic both factually and legally as there are volumes of works identifying the huge steps towards conservation that each of these legislative efforts have provided.
As an example of the basic information simply never provided in the Proposal, the relationship of this effort to other agency efforts is never clearly addressed, as the Proposal seems to focus on conservation leases and planning but never defines the relationships that these concepts have to the sale of carbon credits. The concept of a conservation lease is far wider in scope and possible applicability than leases to create carbon capture credits and these differences are exemplified by the fact the US Fish and Wildlife Service already is already allowing conservation credits to be developed and used by the party developing the credit.[10] The USFWS effort use tools such as land swaps in the conservation efforts and exists as part of a decades long effort that has engaged the public and involved multiple Congressional approvals. The USFWS credits are driven by project type efforts with willing property owners on private lands over a rather long period of time instead of immediate credits being developed on public lands at a large scale. The Organizations are reasonably familiar with the strengths and weaknesses of this type of model as we have participated in panel discussions on this issue with the Western Governors Association. The Organizations have also explored the applicability of USFWS credits in an endangered species reintroduction situation as well. The USFWS effort use tools such as land swaps in the conservation efforts and exists as part of a decades long effort that has engaged the public and involved multiple congressional approvals. The Organizations are also aware that California Air Resources Board has been providing carbon offset credits for conservation efforts for a period and we must ask how this effort would be integrated with the CARB program. These collaborative efforts of CARB and USFWS stand in stark contrast to the Proposal in almost every way possible.
Clearly describing what is being proposed and its relationships to other efforts is going to be critically important to the success of this effort and many others. The relationship the proposed conservation credit leasing program to the existing USFWS program is an example of this type of problem. Is the desire to have BLM administer carbon credit leases and USFWS will expand their existing private lands credit program to create a general conservation credit program on federal public lands? This is a major concern as our efforts should not have to face expanded administrative burden to obtain these credits. Clearly having to obtain carbon-based credits from the BLM and wildlife-based conservation credits from USFWS and other credits from other agencies will create a significant administrative burden for all involved. The possibility of negative impacts to existing partnerships from this type of model is only compounded by the fact the BLM simply cannot hire enough staff to support current efforts.
While clearly defining these two concepts and how they would be integrated with new efforts was not included in the Proposal, clearly defining these concepts is critically important to our interests given the wide range of projects and efforts our community is involved with on public lands. This lack of clarity would be problematic on projects such as moving a trail network outside a drainage that was recently identified as habitat for an endangered species of fish. Clearly a project such as this would be within the scope of a generally applied conservation credit, but would a project such as this would probably not be sufficient to support a carbon offset credit. Failing to address basic questions such as this puts any planning effort on a weak foundation and is detrimental to any possible long-term success.
2(c). Definitions of foundational terms in the Proposal are often not provided or are overly broad and ambiguous which will prohibit implementation of the Proposal.
Throughout the Proposal foundational terms and concepts simply are never defined or meaningfully addressed and the Proposal appears to create distinctions that exist only on paper to further the Proposal. As previously noted, EU researchers have specifically advised against conservation efforts at this level without clear, concise and accurate definitions as they found definable definitions in any project is critical to its long-term success. Without clear and identifiable terms in definitions this entire process will simply become another reason or tool to push uses a certain group does not support off the landscape. This will create immense conflict between interests that may be collaboratively addressing issues currently. This portion of the comments is provided not as an exhaustive list of all poorly defined terms but rather as examples as there are too many terms with vague or incomplete definitions to address. This is compounded by the fact that often terms and their usages are changed simply to suit certain a particular portion of the Proposal. This is a problem that again directly undermines the possibility of long-term success of the Proposal as any implementation of these concepts in subsequent NEPA would be almost impossible.
Organizational concerns around poor definitions and the varying scope of the Proposal start from the position that after reading the proposal several times, we are unable to clearly state if the Proposal seeks to create a conservation lease or a carbon offset lease. These are inherently different concepts that are simply not interchangeable. While all carbon credits may generally be a conservation credit, not all conservation credits are carbon based. An example of why this type of clarity is critical would involve a project repairing or remediating habitat for an endangered species. While this effort is worthy of a conservation credit, it might negatively impact carbon emissions in the area in the short term, as exemplified by the fact heavy machinery may be used for to obtain the conservation credit. The Proposal should address these types of possibilities and how they would be resolved. Would a project such as this need a carbon credit to proceed in obtaining a conservation credit? Would a project like this simply be provided less conservation credits? Providing this type of basic clarity to the effort is important to the success of the program and avoiding unintended impacts. The failure to provide guidance on the basic scope and direction of the Proposal expands as the Proposal fails to address how any credits would be allocated or developed, which will be critical in any NEPA efforts occurring in implementation.
Concerns over the varying scope of the Proposal are compounded by the fact that when a definition is provided it is horribly open ended and arbitrary. The provisions defining causal factor for the conservation effort and discussing application of §6103.1-(2)d is a perfect example of this situation.[11] Rather than an activity to be addressed with the lease being THE causal factor of the problem believed to be occurring and the issue for the lease, the conservation effort only needs to establish that the issue is A significant causal factor to the issue being managed. Clearly the Proposal could provide general guidance that a causal factor must be at least 50% of the factors creating the problem to be addressed. The Proposal provides no discussion as to what “significant” really means or how this would limit the scope of the lease actions in relation to multiple uses operating in the area. This type of open-ended definition could be applied to any issue at any location at any time, and as a result functionally results in a definition that could be applied anywhere and fails to reflect multiple uses. While these concerns may seem remote currently, these will be unresolvable barriers in subsequent NEPA efforts and collaboratives. Efforts like protecting critical habitat for an endangered fish may only be addressing a watershed of a few thousand acres but benefitting an endangered species immensely. How would this be comparatively valued to a restoration in a burn scar impacting hundreds of thousands of acres?
The arbitrary nature of the Proposal and any definitions provided is compounded by the fact the Proposal seeks to apply horribly circular analysis to critical processes for the development of the planning process. Often these circular analyses are applied to existing programs and efforts, causing us concern for the engagement of existing efforts in any conservation leasing program. Again, the Proposal really provides no information or insight into the question being presented for public comment. This problem is exemplified by the following provisions:
“The proposed rule also addresses restoration of degraded landscapes. It offers a new tool, conservation leases, that would allow the public to directly support durable protection and restoration efforts to build and maintain the resilience of public lands. These leases would be available to entities seeking to restore public lands or provide mitigation for a particular action. They would not override valid existing rights or preclude other, subsequent authorizations so long as those subsequent authorizations are compatible with the conservation use. The proposed rule would establish the process for applying for and granting conservation leases, terminating or suspending them, determining noncompliance, and setting bonding obligations.”[12]
Basic questions such as: “What is a degraded landscape?” or “How the multiple use mandate would be integrated into the identification of degraded landscapes?” or “What relation new efforts would have to existing management?” simply is never mentioned. These types of questions are critical to public understanding of the Proposal and any subsequent implementation yet the Proposal fails to provide any guidance on “range of management” actions that might be available to protect intact landscapes. We are forced to assume that the “range of management” action under the lease would be subject to different requirements when applied to a Congressionally designated Wilderness in comparison to a Congressionally designated Special Recreation Management Area for motorized recreation. While our example is comparing Congressional designations, existing management has a wide range of other designations that compound problems understanding the limits of the “range of management” applied in remediation and future management of the area. Would management of motorized recreational opportunities be allowed in an ACEC designated to manage issues completely unrelated to motorized usage, if that area was now subject to a lease or now within a landscape to be protected? The Proposal fails to provide any guidance on questions such as this that will be critical to the successful implementation of the Proposal.
The immediate failures of basic definitions and consistent scrutiny of terms in the Proposal results in guidance for public comment that is entirely circular in nature or is so lacking in context it fails to stimulate public comment. The astonishingly cyclical nature of this problem is exhibited by the fact that the Proposal is seeking input on how a relationship would be developed or applied on the ground but provides no guidance on basic terms and concepts. Without guidance on how these concepts would be related to existing efforts, how can any discussion subsequent have any value at all? In a timelier concern to the Proposal, how is the public even supposed to begin to comment on a concept such as this. While this “range of management” type guidance is critical to success on the ground, it is never addressed and as a result the public cannot comment at all.
The failure to provide a solid foundation for management decision making creates immense problems beyond stimulating public comment when processes are moved slightly further into any subsequent NEPA planning process. The conflict that results from moving further into a NEPA type analysis simply cannot be overstated. Once the process for creation of credits or new ACEC is established, questions such as who would decide what are and are not within an acceptable “range of management” actions or other authorizations that might conflict with conservation values must be addressed. Without a foundation of analysis, decisions such as this are impossible to make for any local managers. This type of ambiguity can have significant long-term impacts like the challenges we continue to have with areas that were at one time inventories for wilderness characteristics and found to be unsuitable for a variety of existing usages. These WSA areas were never suitable for designation but continue to be managed as if they were more than 50 years after the original inventory. This is not a position we want to see repeated for any issue in the future.
As an example of a foundational definition that simply is not provided would be the concept of an “Intact landscape” which is defined as follows:
“Intact landscape means an unfragmented ecosystem that is free of local conditions that could permanently or significantly disrupt, impair, or degrade the landscape’s structure or ecosystem resilience, and that is large enough to maintain native biological diversity, including viable populations of wide-ranging species. Intact landscapes have high conservation value, provide critical ecosystem functions, and support ecosystem resilience.”[13]
Candidly, the Organizations are simply not able to apply this definition to any situation that has been identified to allow for an even generalized understanding of the concept sought to be defined. Is an intact landscape a standard that would be applied on a species-by-species basis or averaged for multiple species? How would this relate to modeled but unoccupied habitat for a species? What is a disruption of an ecosystem? While this definition is critical to any NEPA or planning implementation in the future, no guidance is given.
Another example of the poorly identified and generally vague use of definitions in the Proposal that will hugely impact implementation is provided by the definition of “Unnecessary or Undue degradation” means
“harm to land resources or values that is not needed to accomplish a use’s goals or is excessive or disproportionate.”[14]
Again, the definition provides no hard standards of comparison and could be applied on almost any acre of BLM owned lands, making the value and effectiveness of the definition questionable.
The overly broad and generally diverse nature of the Proposal immensely expands our concerns around definitions, as we are unable to identify a particular component of the Proposal that the definition will apply to. Is this a definition a new definition to be applied for ACEC development or is this a definition to be applied for conservation leases? What are the relationships of this definition to various statutory definitions? Again, these are foundational problems that must be resolved in the Proposal before any meaningful public comment can be obtained. This is disappointing as there are concepts that could be of value for the motorized community.
Implementation problems for managers attempting subsequent NEPA analysis are compounded by the confusion of basic well understood terms by the Proposal. The concept of a “lease” is largely inapplicable to many of the efforts we undertake and probably many other multiple uses that are performing conservation already and many existing management designations. Proposal concepts like “large” are not even tied to a concept to be defined, so we must ask if it is large site-specific project or a large intact landscape or if the concept is limited to BLM lands only or public lands or public and private lands in the planning area. Providing any meaningful comment on implementation of these definitions is made even more difficult as the public is unsure if we are commenting on a conservation credit or a carbon credit or a new ACEC or conservation as a use of public lands.
While no guidance is provided on new issues like conservation credits that are outside existing planning, these are critical to understanding how the intact landscape requirement would be applied to carbon and conservation credits. This is important for us as many of the projects we fund and support are not landscape level efforts but are targeting more localized concerns that provide concrete identifiable benefits to a species or resource. These are critical questions that must be addressed as clarity on these types of problems will avoid significant unintended consequences moving forward. The Organizations would be remiss in not recognizing the fact we are still fighting over the concept of untrammeled by man more than 50 years after that management concept was introduced. This type of problem must be avoided.
The failures of proposed definitions greatly complicates understanding how these new standards would be applied across various existing management prescriptions. There simply is no guidance on how existing management determinations would relate to subsequent management decisions if an area has been subject to unnecessary or undue degradation. Automatically assuming this determination can be supported by a single management standard, such as an ACEC, would be premature at best. Active management response to serious problems may be impaired by a designation of an ACEC or similar designation, and these conflicts will create nothing but massive conflict in NEPA efforts during implementation while creating little to no benefit. Efforts like protecting critical habitat for an endangered fish may only be addressing a watershed of a few thousand acres but benefitting an endangered species immensely. How would this be comparatively valued to a restoration in a burn scar impacting hundreds of thousands of acres? The public needs basic guidance to comment on equitable allocation of credit issues such as this and that has not been provided.
2(d)(1). Conservation has been defined by Congress through the Endangered Species Act and applied to all public lands for decades.
The Proposal further impairs the ability of the public to meaningfully comment on the effort by making assertions that simply are completely incorrect and conflicts with decades of Congressional actions and case law. This problem is exemplified by assertions in the Proposal that appear to seek to redefine conservation into an entirely new concept outside existing Congressional definitions, The Proposal provides the following outline of this concept:
“To ensure the resilience of renewable resources on public lands for future generations, the proposed rule promotes ”conservation” and defines that term to include both protection and restoration activities…… To support efforts to protect and restore public lands, the proposed rule clarifies that conservation is a use on par with other uses of the public lands under FLPMA’s multiple-use and sustained-yield framework” [15]
The immediate conflict of this position and the legal requirements for public lands management is exhibited by the fact Conservation has been defined by Congress since 1973 as part of the Endangered Species Act. The ESA provides the following definition of conservation:
” (3) The terms “conserve“, “conserving“, and “conservation” mean to use and the use of all methods and procedures which are necessary to bring any endangered species or threatened species to the point at which the measures provided pursuant to this chapter are no longer necessary. Such methods and procedures include, but are not limited to, all activities associated with scientific resources management such as research, census, law enforcement, habitat acquisition and maintenance, propagation, live trapping, and transplantation, and, in the extraordinary case where population pressures within a given ecosystem cannot be otherwise relieved, may include regulated taking.”[16]
The immediate problem with the Proposal that is unresolvable is the ESA is one of the few statutory requirements that elevates conservation above multiple uses and is fully applicable on every acre of land that BLM managers. The application of the ESA in this manner was again clearly and directly stated by the USFWS in their June 28, 2023 final regulations governing the designation of experimental species populations as follows:
“The purposes of the Endangered Species Act (ESA; 16 U.S.C. 1531 et seq.) are to provide a means to conserve the ecosystems upon which listed species depend, to develop a program for the conservation of listed species, and to achieve the purposes of certain treaties and conventions. Moreover, the ESA states that it is the policy of Congress that Federal agencies shall seek to conserve threatened and endangered species and use their authorities to further the purposes of the ESA (16 U.S.C. 1531(c)(1)).”[17]
It is certainly not unreasonable to ask that the two agencies within the DOI align on foundational points such as if conservation is a use of public lands. That clearly has not happened. Every BLM NEPA analysis must go through a Section 7 consolation to ensure conservation of the species under the ESA is achieved before multiple uses are even thought about. The application of the ESA is a “use of public lands” in every sense of the concept despite the repeated assertion that conservation is not a use. Not only is conservation a use of public lands, this is the ONLY use that is elevated above other multiple uses for protections.
The public is simply unable to comment on any assertion of the Proposal that conservation is not defined and is not a use on public lands as Congress has specifically elevated conservation above multiple uses in numerous situations. Rather than providing insight on how would these interpretations of conservation be aligned, the Proposal simply moves past this challenge, resulting in another elephant of an issue being relegated to a mouse hole. The Organizations doubt that the Proposal is seeking to alter the application or scope of the ESA or USFWS management authority. While the ESA definition of conservation largely aligns with the generally understood definition of conservation, this is again a foundational problem which is created by the Proposal seeking to twist existing concepts and legal mandates to achieve its goals. Again, this conflict may appear minimal in the Proposal, it will be an unresolvable barrier to NEPA or further implementation of the Proposal. The public cannot substantively comment more on this conflict than to identify it in our comments.
2(d)(2). Conservation has been mandated by Congress for decades through the Congressionally created NLCS program.
Even disregarding the failure of the Proposal to address the conflict of its provisions and the ESA, throughout the Proposal contradictory positions are taken and distinctions are asserted to be present that simply cannot be defended when commonly known definitions and understood terms such as “conservation” are used. As noted previously many of these conflicts are simply moved past and when the Proposal chooses to address previous Congressional mandated management requirements this only compounds previous ambiguities we have addressed. Despite not clearly defining conservation in FLPMA or the Multiple Use Sustained Yield Act, Congress has mandated conservation on all public lands for decades outside the ESA and has used a wide range of tools to address these goals with the designation of Wilderness areas, National Conservation Areas, National Recreation Areas, National Preserves, authorization of monuments and through site specific designations such as the California Desert Conservation Area.[18] While conservation may not be specifically defined in these legislative efforts, it is occurring as based on commonly understood definitions of the term and concept.
Historically Congress has chosen to apply the generally understood concept of conservation through their designations and requirements seeking to avoid possible confusion of the term and its application on the ground. Similarly, much of what the Proposal seeks to accomplish falls within the common definition of conservation, which is:
“1: a careful preservation and protection of something especially : planned management of a natural resource to prevent exploitation, destruction, or neglect
water conservation or wildlife conservation
2: the preservation of a physical quantity during transformations or reactions”[19]
There can be no factual argument that everything in the Proposal is conservation when applying the commonly understood and applied definition. Rather than addressing the common definition of conservation in manner consistent with existing Congressional efforts, the Proposal moves to a convoluted discussion of conservation under various programs. This is an immense problem as failing to use commonly understood terms like this will create vast problems in implementation.
An example of Proposal twisting of previous legal mandates would be in the discussion of the National Landscape Conservation System (“NLCS”) which by Congressional definition, does conservation. Again, these are foundational problems that must be addressed. If the desire is to allow conservation mitigation credits, then the Proposal should say that and define how this new concept is outside the traditional conservation definition. For reasons that are never explained, the Proposal asserts that conservation within the NLCS is somehow different than conservation outside the NLCS. This distinction is simply not supported in any manner by the history of Congressional efforts around the NLCS. NLCS efforts were originally created more than 20 years ago by Secretarial Order from Secretary Bruce Babbitt. This Office’s mission was formalized by Omnibus Public Lands Act of 2009 which mandated the following mission for the NLCS as follows:
“(a) ESTABLISHMENT.—In order to conserve, protect, and restore nationally significant landscapes that have outstanding cultural, ecological, and scientific values for the benefit of current and future generations, there is established in the Bureau of Land Management the National Landscape Conservation System.”[20]
Here Congress chose to identify and expand on the existing understanding of Conservation by requiring these areas to conserve, protect and restore these areas. Again, this is problematic to any assertion conservation is not a use of public land and opens the door to an actual reduction in the protection of these areas. The conflict between the Proposal and the NLCS requirements expands when the NLCS national strategy is reviewed. The NLCS National Strategy is organized around four major themes: 1) Ensuring the conservation, protection, and restoration of NLCS values; 2) Collaboratively managing the NLCS as part of the larger landscape; 3) Raising awareness of the value and benefits of the NLCS; and 4) Building upon the BLM’s commitment to conservation. [21] This strategy clearly states as follows:
“All NLCS units are designated in keeping with an overarching and explicit commitment: to conserve, protect, and restore natural and cultural resources as the prevailing activities within those areas, shaping all other aspects of management. To provide for uses that are compatible with landscape and resource values, NLCS managers will: • Focus on conservation as the primary consideration in planning for and management of NLCS lands, consistent with designating legislation. • Develop baseline information on NLCS lands through assessment, inventory, monitoring, evaluation, and scientific study. • Base planning and decision making on a scientific foundation using next generation management tools. • Promote the NLCS as an outdoor laboratory and demonstration center for new and innovative management and business processes. • Provide for compatible uses consistent with the legislation designating each unit and in collaboration with surrounding communities and interest groups. • Plan and manage NLCS facilities with an eye to protecting resources, serving the public, and supporting local communities.[22]
This is by definition conservation and there are benefits to these efforts beyond mere on the ground management. It has been the Organizations experience that the NLCS designations allow managers to obtain more internal funding to protect and improve resources within the NLCS areas. Often times the NLCS designation also allows outside funding to be more accurately targeted to these values as well. Indirect benefits of these efforts could be greatly impacted by the Proposal and again simply are not even mentioned.
The failure of the Proposal to provide calculation and recognition of the success of NLCS program in conservation efforts is problematic for other provisions of the Proposal, such as assertions of large-scale expanding impacts to public lands. This problem is not resolved by assertions NLCS efforts are not conservation but rather by developing a Proposal that accurately discusses what the effort is seeking to develop and how it would relate to existing efforts and planning.
The successful conservation efforts under the NLCS program are not even accurately reflected in the Proposal but rather are overlooked and a second new poorly defined processes is found to be necessary for future planning. This second concept the inclusion of land health standards. The Proposal provides no information on land health standards and how this would relate to the range of management actions now available rather the Proposal states something very different as follows:
“The proposed rule provides a framework to protect intact landscapes, restore degraded habitat, and ensure wise decision making in planning, permitting, and programs, by identifying best practices to manage lands and waters to achieve desired conditions. To do so, the proposed rule applies the fundamentals of land health and related standards and guidelines to all BLM managed public lands and uses; current BLM policy limits their application to grazing authorizations.”[23]
The describing the relationship of the new concept of a land health standard and existing conservation is immensely important for implementation. Rather than trying to resolve this problem, the Proposal then seeks to create a distinction between NLCS conservation and conservation under the Proposal as follows:
“Section 2002 of the Omnibus Public Land Management Act of 2009 (16 U.S.C. 7202) legislatively established the National Landscape Conservation System (NLCS), to include public lands carrying certain executive or congressional designations and set parameters for the management of lands within the system. NLCS lands are subject to regulatory requirements like other BLM-managed public lands. The regulations proposed here define the term ”conservation” in a way that is distinct from the use of the term in section 2002. Here, ”conservation” is a shorthand for the direction in FLPMA’s multiple-use and sustained-yield mandates to manage public lands for resilience and future productivity. ”Conservation,” as the term is defined in these regulations, is part of the BLM’s mission not only on lands within the NLCS, but on all lands subject to FLPMA’s multiple-use and sustained yield mandates. At the same time, these regulations also would support the BLM’s execution of the statutory direction in section 2002 to ”manage the [NLCS] in a manner that protects the values for which the components of the system were designated” (16 U.S.C. 7202(c)(2)).”[24]
The inclusion of a second planning concept in this discussion of conservation only creates more confusion and ambiguity. We are unable to understand what the basic direction and intent of the land health provision is or how we could ever assert there was success in achieving this goal. Would we agree that NLCS lands are no longer multiple use? Yes, as often certain activities are not allowed on Congressionally designated lands managed under the NLCS process. We would also agree that NLCS lands may have a heightened emphasis on conservation as other activities are prohibited. This is conservation under the commonly understood definition of conservation. We are unable to understand how these conclusions align with the desire to include new planning tools in BLM management moving forward.
Despite assertions that conservation under the Proposal is different than previous conservation efforts, the Organizations are unable to understand how conservation under NLCS and conservation under Proposal are any different from the generally accepted definition of conservation. While they may be comparing to a slightly different baseline, the efforts are still conservation. The arbitrary and highly variable definition of conservation in the Proposal is directly conflicting with the understanding of conservation in almost every other statutory action to date. The confusion and ambiguity of the Proposal on the conservation issue is compounded with the integration of the new concept of land health standards which compounds confusion as the relationship of land health standards to existing planning is never addressed. This is highly frustrating to partners that have worked hard for the success of conservation and recreation efforts on numerous NLCS parcels and also failures to accurately describe the basis of the effort provides an exceptionally poor foundation for a new planning effort.
2(e). FLPMA has woven conservation throughout the planning process with the ACEC development process.
The failure of the Proposal to define terms and concepts consistently and accurately has led to assertions and distinctions that make no sense for implementation efforts. The impact that these failures have on our ability to substantive comment on the Proposal are immense. The impact of these failures is exhibited by the discussion of the ACEC process in the Proposal and assertions that conservation under the ACEC process is different than conservation under the NLCS process or conservation under other statutory requirements such as the ESA. The only difference we are able to identify in the NLCS process and the ACEC process is the fact that ESA driven conservation and NLCS designations are generally provided by Congressional action and ACEC designations are created through the RMP development process as required by Congressional actions that have been passed into law. These are distinctions that exist on paper only.
The failure of the Proposal to even address problems such as paper only distinctions is exhibited in the following provisions:
“Finally, the proposed rule would amend the existing ACEC regulations to better ensure that the BLM is meeting FLPMA’s command to give priority to the designation and protection of ACECs. The proposed regulatory changes would emphasize ACECs as the principal designation for protecting important natural, cultural, and scenic resources, and establish a more comprehensive framework for the BLM to identify, evaluate, and consider special management attention for ACECs in land use planning. The proposed rule emphasizes the role of ACECs in contributing to ecosystem resilience by providing for ACEC designation to protect landscape intactness and habitat connectivity.”[25]
The Organizations are very frustrated at the amazingly narrow explanation of the planning process that is provided in this Proposal. Under BLM processes, any member of the public can propose an ACEC on any portion of BLM lands for any reason during the creation of an RMP. The nomination process simply cannot be broader than this. Through the RMP process, many of these citizen-based proposals are not moved for a variety of legal and factual reasons and often this analysis can span hundreds of pages of highly site-specific analysis in the EIS. While the Organizations have participated in thousands of these planning efforts, we have never seen this type of site-specific planning analysis not address a citizen proposed ACEC on the basis that BLM lacks authority to do conservation or that conservation is not a use of BLM lands. Any landscape level assertion to the contrary undermines the highly site-specific analysis of these proposals that has already occurred. While the ACEC planning process is very open ended, we do not contest that in many areas RMPs are horribly out of date and need to be updated. This problem is simply never mentioned in the Proposal and we are very concerned that the Proposal will compound the impact of staffing shortages rather than ease these issues.
For the BLM, there can be no better foundational starting point than understanding the existing statutory management requirements for conservation efforts primarily using the ACEC process which are:
Ҥ1701. Congressional declaration of policy
(a) The Congress declares that it is the policy of the United States that—
(8) the public lands be managed in a manner that will protect the quality of scientific, scenic, historical, ecological, environmental, air and atmospheric, water resource, and archeological values; that, where appropriate, will preserve and protect certain public lands in their natural condition; that will provide food and habitat for fish and wildlife and domestic animals; and that will provide for outdoor recreation and human occupancy and use;
(11) regulations and plans for the protection of public land areas of critical environmental concern be promptly developed;” [26]
Legally, conservation has always been included in every step of planning in the FLPMA legislation and specifically required in development of various planning documents. Any assertion to the contrary would ignore thousands of pages of site specific NEPA analysis of the ability of areas to be managed for ACEC characteristics. Any assertion of ACEC designations being underused ignores the fact that including the ACEC concept in FLPMA in 1976 was a significant change for the BLM management, as prior to FLPMA the need for conservation on BLM lands was significantly reduced. The Proposals attempts to redefine the scope of the regulations appears to be an exercise that leads to nothing other than repeating existing authority and attempting to create distinctions that exist only on paper. Any assertion that conservation is not a use of the lands outside of ACEC designations, is simply off point as conservation is a concept that has been woven throughout almost every planning statute in modern time. Again, this is an effort to create a planning distinction without any actual difference. This lack of a distinction is exemplified by the failure of the Proposal to identify the differences between the conservation efforts provided by an NLCS designation and an ACEC designation and how these are different from conservation under the ESA. These are distinctions on paper only.
In the implementation of FLPMA planning requirements, ACEC inventory efforts often spans hundreds of pages of site-specific analysis in planning efforts. BLM regulations specifically outline how Field Offices must be fully inventoried and a robust public process is provided for in the development and management of ACEC designations in the development of an RMP. ACEC designated areas have always been areas where conservation is the use of these lands, which makes any assertion of a need to elevate conservation as a use in the proposal problematic. BLM regulations explicitly outline the ACEC process as follows:
“02 Objectives. ACEC designations highlight areas where special management attention is needed to protect, and prevent irreparable damage to, important historic, cultural, and scenic values, fish, or wildlife resources or other natural systems or processes; or to protect human life and safety from natural hazards. The ACEC designation indicates to the public that the BLM recognizes that an area has significant values and has established special management measures to protect those values. In addition, designation also serves as a reminder that significant value(s) or resource(s) exist which must be accommodated when future management actions and land use proposals are considered near or within an ACEC. Designation may also support a funding priority
- 03 Authority. The Federal Land Policy and Management Act (FLPMA) provides for ACEC designation and establishes national policy for the protection of public land areas of critical environmental concern. Section 202(c)(3) of the FLPMA mandates the agency to give priority to the designation and protection of ACEC’s in the development and revision of land use plans. The BLM’s planning regulations (43 CFR 1610.7-2) establish the process and procedural requirements for the designation of ACEC’s in resource management plans and in plan amendments”[27]
Again, the Organizations must question any legal assertion that conservation is not a use under the multiple use mandate requirements, as the ACEC designation is clearly a use of public lands. Conservation efforts are not just limited to the designation of ACEC areas but are woven throughout the planning process and further supplemented by the Section 7 consultation process required under the Endangered Species Act. Understanding and clearly reflecting existing requirements on public lands will be a critical component of any conservation leasing effort and the allocation of conservation credits for services already provided. Any discussion of issues such as this would have led to identification of problems in implementation such as is this a carbon credit conservation lease or a more generalized conservation credit program. If this is a more generalized conservation credit discussion, does this mean that existing USFWS credit programs will be expanded? If these basic issues are not accurately addressed in the planning process, interested parties will be overlooked and unintended impacts will be immense. Again, this is completely unacceptable to the Organizations.
2(f). Executive Orders requiring travel management processes and the development of the minimization criteria are conservation.
The obligations to perform conservation efforts on BLM lands is not just statutorily created, as significant conservation has been required by Executive Orders(“EO”). It is again problematic that the Proposal assert to be applying mandates of several EO in the development of the Proposal, but fail to provide any summary of existing mandates created by other EO. Understanding the multiple basis of conservation will be integral to the relationships between various interests under the Proposal. Without basic understanding of why decisions have been made will be critical in avoiding repetition of efforts and reducing unintended consequences of any action. An example of existing obligations to perform conservation on ALL BLM lands related to a particular use in place for more than 50 years is the minimization review for travel planning mandated by EO 11644 originally issued by President Richard Nixon in 1972. Executive Order 11644 specifically provides as follows:
“Sec. 3. Zones of Use. (a) Each respective agency head shall develop and issue regulations and administrative instructions, within six months of the date of this order, to provide for administrative designation of the specific areas and trails on public lands on which the use of off-road vehicles may be permitted, and areas in which the use of off-road vehicles may not be permitted, and set a date by which such designation of all public lands shall be completed. Those regulations shall direct that the designation of such areas and trails will be based upon the protection of the resources of the public lands, promotion of the safety of all users of those lands, and minimization of conflicts among the various uses of those lands. The regulations shall further require that the designation of such areas and trails shall be in accordance with the following–
(1) Areas and trails shall be located to minimize damage to soil, watershed, vegetation, or other resources of the public lands.
(2) Areas and trails shall be located to minimize harassment of wildlife or significant disruption of wildlife habitats.
(3) Areas and trails shall be located to minimize conflicts between off-road vehicle use and other existing or proposed recreational uses of the same or neighboring public lands, and to ensure the compatibility of such uses with existing conditions in populated areas, taking into account noise and other factors.
(4) Areas and trails shall not be located in officially designated Wilderness Areas or Primitive Areas. Areas and trails shall be located in areas of the National Park system, Natural Areas, or National Wildlife Refuges and Game Ranges only if the respective agency head determines that off-road vehicle use in such locations will not adversely affect their natural, aesthetic, or scenic values.”
Again, this type of a requirement in planning is conservation by definition. The Organizations repeat our concerns around the accuracy of any assertion that the agency lacks authority to undertake conservation actions as this is another example of how conservation is woven throughout the planning process. As we have outlined in other portions of these comments, the motorized recreational community has proceeded well beyond a minimalist interpretation of compliance with this mandate. Rather our programs have sought to avoid as many issues as possible and as a result could be generating credits already through these efforts. This is conservation efforts in balance with recreation working to improve both on the ground.
Understanding the relationship of various Statutory requirements, Executive Orders and other existing planning efforts is important to avoiding conflict as well as it appears many of the interests that seek to enter the conservation credit market are unfamiliar with the multiple use mandate of federal lands as they have not done projects on federal lands previously. Leaseholders should be able to understand that closing public access to perform conservation under a lease conflict with other planning that has specifically found the route sustainable. The leaseholder should not be allowed to violate those travel planning decision by asserting that closing the route, even temporarily, is a benefit to conservation. Understanding these issues and multiple processes addressing conservation on the ground will allow accurate allocation of conservation credits across existing efforts and avoid unintended impacts to parties outside of any lease.
3(a). Use of public lands management as a saleable commodity must be done equitably and undoubtedly requires Congressional approval.
The Organizations cannot view the proposed concept of a Conservation Lease and conservation as a use of public lands in the isolation of the Proposal, given that there are numerous legislative Proposals pending that would create and expand this concept on public lands.[28] As an example is the provisions of §137 of America’s Outdoor Recreation Act, which would provide similar leasing authority to the USFS as is proposed here. This is not a coincidence and indicates that the Proposal is the first step towards monetizing public lands management to develop conservation or carbon credits that can be bought and sold by the holder of these credits. We are not opposed to this concept being applied on the use of public lands for the development of conservation credits as we can see benefits to the OHV community from this type of effort. However, we assert any credits must be equitably allocated across all efforts and not just those seeking to sign leases.
As previously mentioned, USFWS already has a conservation credit market in place for endangered species efforts, which is not addressed in the Proposal. There are also many State led efforts which could easily be expanded allowing the public to capture conservation credits for efforts they have undertaken on federal lands. An example of this type of program would be the credit program existing with the California Air Resources Board, which we must believe could merely be expanded to include projects on federal lands. This type of benefit would have to be achieved through a program that is legal and equitable for all efforts that could be creating conservation credits. We are concerned that conservation leasing is simply not a model or vehicle for the creation of conservation credits on public lands we can support as it is not equitable to all interests that might be performing work deserving of credits. The Proposal entirely fails to provide any guidance on how credits would be created and allocated in long term projects or across multiple management agencies. The Proposal also fails to address how provisions of the lease that are proposed would be managed, which is a major concern for us as third-party lease holders will have no incentive to comply with multiple use mandates other than public pressure and litigation as BLM entirely lacks staff for this type of effort. The public should not be forced to sue a third party to keep access to federal public lands.
The Organizations are also concerned that an effort of this type of scale is probably not best vetted through a small provision of an agency planning effort. This is a huge initiative and needs to be meaningfully discussed with all participants. The carbon credit trading market appears to be driven to monetize conservation efforts in an effort to increase funding and possibly use credits to offset other impacts in other areas. Our research indicates that just the carbon credit market estimated to be an $850 billion global market and rapidly growing in size. The sheer size of the interests involved in this effort is concerning as it will put many interests of hugely disproportionate size in conflicting uses on federal public lands. For purposes of these comments, we are referring to these efforts as a “conservation credit program.” The primary nonpublic conservation credit program we are aware of is the Nature Conservancy’s Naturevest effort, which is a conservation effort driven by JPMorgan/Chase through the Nature Conservancy. The Organizations believe the change from a quasi or entirely governmentally run conservation credit program is significantly different than one largely run by a private entity on lands without a multiple use mandate. While there are other players and entities working in the conservation credit sector, Naturevest is simply the privately based program we are most familiar with and able to locate the most information regarding. We are referring to the privately run conservation credit model as the Naturevest model simply for clarity of efforts.
Naturevest is a partnership formed in 2014 which now claims more than $2.5 billion spent in last decade in a global effort that largely focused on carbon-based credits. The conservation credit programs appear to be predominately a for-profit effort partially seeking to create carbon credits to sell through expanded “protections” on landscapes. Based on our investigations it appears the Naturevest model program does not focus on any actual on the ground benefits and the creation of conservation credits appears to be very theoretical in nature. As an example, the Naturevest effort identifies several major international debt restructuring efforts for countries, such as their efforts in Belize where JPMorgan efforts to restructure of national debt generated protected aquatic habitat. Very little information is provided on how the protection functions or the benefits that are achieved from these protections, making any comment on how these benefits interact with other interests impossible. Another highlighted project was the protection of forests in Pennsylvania from timber harvest which creating credits by “protecting” trees in State Forest. Subsequently the State of Pennsylvania stated that were never proposed to be cut in the first place. The accuracy of any asserted benefits has been the topic of significant debate as many analysists are concerned around the foundational assumptions of the credit effort in general.[29] This type of foundational concern should be resolved prior to any conservation lease initiative being moved forward. If conservation benefits are claimed, they should be accurately calculated, provide protection in perpetuity and be equitably available.
While the long-term viability of conservation benefits may be a weakness of the Naturevest model of conservation credits, it is a strength of statutorily created programs like the OHV efforts. As a result of these statutory basis the long-term benefit of any effort is far more identifiable and consistent as grant program funded efforts can provide maintenance for these benefits almost indefinitely moving forward. Not only are benefits more identifiable and sustainable, State OHV programs investments exceed the value of contributions from efforts like Naturevest at the national level. Annually State OHV/OSV programs are providing $200-$300m for public lands and access across the nation and are overwhelmingly funded by voluntarily created OHV registration programs. These are programs where the primary funding is the result of legislation was passed by the users to self-tax themselves to protect resources and access and are unique to the motorized trails community. Global annual spending of Naturevest is roughly similar in size to benefits of voluntary motorized registration programs across country over the same time.
While OHV efforts are primarily associated with recreation, significant portions of the funding are protecting resources that should be the basis for some type of credit. These programs provide benefits that are very different than the abstract benefits of the conservation credit programs as we focus on tangible on the ground improvements rather than speculative benefits that may never occur. As an example of the projects we undertake to protect resources, our crews build bridges, install culverts and harden trail tread to protect resources.

Our crews also proactively address drainage issues from weather impacts to protect aquatic resources and habitat on public lands in partnership with BLM managers after NEPA analysis is completed.

Our clubs and crews install educational signage to avoid impacts before they happen and width restrictors to ensure that larger vehicles are not traversing narrow trails and possibly causing impacts.

The crews that the OHV programs fund, along with partner clubs cut thousands of fallen trees from trails to allow these routes to provide recreational opportunities. These routes also protect resources as managers can use these routes to respond rapidly and safely to wildfire outbreaks in the area. The following picture represents our efforts in one location.

These are concrete benefits for conservation and sustainability that we also provide ongoing funding for maintenance and monitoring of. If these improvements are impacted by unusually severe weather or other issues, they can be repaired quickly unlike benefits that are abstract or remote from conditions on the ground. The highly valuable nature of these types of efforts was recently highlighted in a 2023 publication from Federal Highways Administration outlining the roles that all forms of trails have in the climate situation and the often-critical role that trails play in addressing sustainability. The FHWA states this conclusion as follows:
“In terms of specific vulnerabilities, future research could focus on the vulnerability of trails to wildfires, particularly on the role the vegetation along the trail may play as fuel for wildfires in urban and semiurban areas. In geographic areas at risk from wildfires, trail designers, planners, and managers will benefit from understanding how trail design and vegetation can be adapted to reduce trail vulnerabilities to the frequency and/or severity of wildfire events.
Additionally, given the recognition that maintenance and management play an important role in reducing trails’ vulnerability to extreme weather, future research could address how those practices should change, now and in the future, to ensure trails’ resilience to increasing and shifting natural hazards.” [30]
Given that Federal Highways has already recognized the benefit of access and trails to climate sustainability, our concerns about the benefits of trails to BLM conservation efforts is well placed.
This foundational differences of these efforts with Naturevest type efforts should be cause for discussion as basic equity of those performing conservation must be provided across different models achieving conservation. The Proposal simply does not provide this type of equity but rather create the situation where existing local efforts developing actual on the ground conservation benefits could be allocated to entities simply holding a least unrelated party to the local effort. The Proposal further allows the situation where a third party could come into an area, execute a conservation lease and then leave without addressing maintenance. Managers would then be forced to use other resources for this, such as an OHV grant, and that grant program might be precluded from obtaining a similar credit-based benefit. This is unacceptable.
OHV concerns around conservation credits created with conservation leases extend beyond mere equity in allocation of credits but are far more foundational. Those participating in the conservation credit market currently do not appear to be working in any market managed under a multiple use mandate on public lands. Our research indicates that the conservation credit market previous efforts have targeted state or private lands that lack a multiple use mandate. This is a major concern as there are no best management practices or other guidance that can be provided to local land managers who are exploring the application of this type of lease in the planning process. This is going to cause a lot of problems and conflicts as managers have never done this type of effort before. We are hesitant to adopt a trial by fire type learning model in this process as we will lose access and many other will be impacted by unintended consequences of the effort. The Organizations are even more concerned that the Proposal states that “temporary” closures to access would be allowed.
Our decades of experience undertaking huge projects that may be subject to creation of a conservation or carbon credit also allow us to understand that many large projects focused on large tangible benefits on the ground are not funded by a single source but are rather a collaboration of many interests, some governmental and others not. Given the common nature of this collaborative model of moving large projects forward, the Proposal must also address if the conservation credits could be allocated across multiple funding sources based on the funding and other resources provided for the project.
3(b)(2). Is the Proposal seeking to create a conservation lease or a conservation permit program?
The introduction of a Naturevest type effort into the management of federal public lands management is an entirely new effort as previous conservation leases have focused on lands without the multiple use mandate. Moving the Naturevest private model to public lands gives rise to another basic question that is not addressed in the Proposal. What public lands management concept most aligns with the desired program and benefits? The answer to type of question may be a conservation permit not a conservation lease. Again, these foundational terms are not identified in the proposal, so the Organizations must use standard definitions of these concepts for our discussion. A lease by definition means:
“Any agreement which gives rise to a relationship of landlord and tenant (real property) ot a lessor and lessee(real or personal property). A contract for the exclusive possession of lands, tenements or hereditaments for life, for a term of years at will, or for any special interest than that of a lessor, usually for a specified rent or compensation. Contract wherein one lets to the other a certain space, property, or building for a specified unit of time, generally a week, month or year. Agreement under which the owner gives up possession and use of his property for valuable consideration and for a definite term and at the end of the term the owner has the absolute right to retake control and use of the property.”[31]
Concepts necessary to create a lease, such as exclusive usage and other legal requirements, simply do not align with the Proposal and protecting multiple uses already in place well at all. What other options might have been looked at as a vehicle to allocate credits with and how was the leasing concept identified as the proper vehicle for this effort to move forward with are simply never addressed. Clearly there are other models available to perform this function.
While the Proposal to review possible options for allocation of credits, making meaningful public comment is difficult to create, the Organizations are able to identify other options for the allocation of credits that are worthy of discussion. The efforts that seem to be reflected in the Proposal are more accurately reflected in the legal concept of a permit rather than a lease, and the permit concept aligns better with the multiple use mandate of public lands. By definition a permit is:
“In general, any document which grants a person the right to do something. A license or grant of authority to do a thing. A written license or warranty issued by a person in authority empowering the grantee to do some act not forbidden by law but not allowable without such authority. A license or instrument granted by officers of excise(or customs) certifying that duties on certain goods have been paid or secured and permitting their removal from some specified place to another.”[32]
While the legal concept of a permit aligns far better with the efforts being undertaken, for reasons that are unclear, this type of option is not discussed in the Proposal. A major benefit of the permit model for conservation efforts when compared to the conservation lease model, is the fact that most permits do not allow exclusive possession of public lands which the permit is issued for. Again, failing to provide definitions and meaningful discussion into basic concepts in the Proposal make it very difficult for us to substantively comment on the Proposal. While a permit might align better with the effort, a large amount of discussion still needs to occur to ensure multiple uses and existing planning are addressed and protected before the Organizations could support even the concept of a permit being the proper vehicle for implementation.
3(b)(2). Best available science also questions if a lease even the correct tool to be used for environmental credits?
One of the foundational conclusions that appears to have been made before the Proposal was released was the determination that a lease was the correct tool for capturing the environmental benefits for any efforts that could arise from the program. This is a major concern for our interests as a lease could actually create a barrier to the efficiency and effectiveness of our efforts moving forward. This is very concerning to us. The determination of the proper tool to be applied for the capturing of possible conservation benefits is generally far from resolved with researchers addressing this question. Rather researchers seem to be involving more and more concepts into efforts to capture benefits to strike the proper balance of credits and efforts. Researchers have recently been summarized as follows:
“To be effective, habitat exchange program must achieve at least no net loss of habitat for target species (zu Ermgassen et al., 2019). Yet data generally are not collected to rigorously assess outcomes. Few habitat exchange programs have been evaluated formally (but see Calvet et al., 2019; Robertson & Rinker, 2010), and the collective ability of habitat exchange programs to offset ecological impacts and achieve conservation objectives has not been assessed. Furthermore, many challenges for biodiversity offsetting programs more broadly are applicable to habitat exchange programs.”[33]
Not only is the basic structure to allocate credits far from resolved scientifically, other questions such as timing of credits being provided and efforts being concluded remains a completely unresolved question. These are challenges we face every day just under a different management structure as our programs must balance the desire to construct a new facility with the ongoing need to maintain existing structures that are already in place. While these are entirely different management models, the challenges are very similar and highlights a VERY different path towards resolution. The Proposal adopts a model that provides no insights regarding the balancing of credits being derived from a third-party leaseholder effort who has ZERO incentive to maintain any of their efforts in the long term under the current Proposal. In stark contrast, our funding programs are statutorily created through state legislative efforts, which means our resources are available to perform the original effort creating the benefit and to ensure that the benefit continues to be provided indefinitely into the future. This situation has plagued those seeking to sell or buy credits, which researchers have outlined as follows:
“This notwithstanding, there is an important critical debate in the scholarly literature. Overall, a main critical argument is that the goal of no-net-loss is rarely reached (Gardner et al., 2013; Levrel et al., 2017) and that monitoring and evaluation of implemented offsets is poor Again the Organizations must insist that foundational questions of equity around the basic structure and performance of any conservation credit market (Vaissiere et al, 2017).”
These foundational challenges to basic equity and long-term success of any conservation credit effort that may be developed must be resolved before implementation begins. This can help avoid profound impacts on existing partnerships, multiple uses more generally and ensure that benefits are maintained in the future. These types of concerns are neither abstract or remote to our concerns, as resolution of these questions must reflect the strengths and weakness of efforts into an equitable allocation of any credit that may be developed or sold. Basic questions must be resolved before implementation to ensure the party funding and performing the mitigation effort is the one that is receiving the credit. Credits should not be being provided to a third party that is simply holding the lease and doing nothing on the ground. The Organizations would like to avoid having to maintain or fix poorly developed mitigation efforts that were performed by third parties who are no longer interested simply to maintain our access to these areas. This is patently unfair.
3(c). Does BLM even have the statutory authority to enter into conservation leases?
While there is no question that BLM has been required to perform conservation in all phases of management for decades, this existing statutory authority does not appear to include utilizing leases to achieve these benefits. The Proposal fails identify even arguable statutory authority for BLM to enter into a lease of this type. By law, BLM does not inherently have the authority to enter into any lease but rather this authority is provided to the BLM by Congress. Often these grants of authority come with clear goals and objectives for a lease and a mandatory public process to be complied with to ensure the multiple use mandate is complied with. BLM authority for the issuance of mineral leases is authorized by 1920 Mineral Leasing Act which requires NEPA. BLM issuance of grazing leases is authorized by FLPMA, which again requires significant planning and public engagement efforts under NEPA. While there are several other provisions that allow disposal of lands by the BLM to generate funds for reinvestment, they are not addressed here as the Proposal does not mention the disposal of public lands
BLM is also authorized to undertake various land disposals and leases under the Recreation and Public Purposes Act of 1926, which again requires NEPA and compliance with numerous other provisions, such as the identification of lands for leasing in the development of an RMP. As the conservation credit effort clearly is not a mineral extraction effort or involves grazing cattle, we must assume the effort is thought to be a public purpose. While BLM appears to assume that a conservation lease is a public purpose conceptually, it does not fit with the definition of a public purpose in the CFR. This definition is:
“Public purpose means for the purpose of providing facilities or services for the benefit of the public in connection with, but not limited to, public health, safety or welfare. Use of lands or facilities for habitation, cultivation, trade or manufacturing is permissible only when necessary for and integral to, i.e., and essential part of, the public purpose.”[34]
The Organizations do not contest that the concept of a conservation lease may be a public purpose, the Organizations also submit that a conservation lease simply does not fit that definition well at all. It is against the scope of a statute that is more than 100 years old the Organizations must raise serious concerns over the application of this statute in the manner proposed by BLM. Courts have approached this question with growing scrutiny as last month the US Supreme Court again reaffirmed their position on the ability of an agency to expand and alter their Congressionally provided scope of authority on any issue as follows:
“But “construing statutory language is not merely an exercise in ascertaining ‘the outer limits of a word’s definitional possibilities… and here, “only one . . . meanin[g] produces a substantive effect that is compatible with the rest of the law,” We have often remarked that Congress does not “hide elephants in mouseholes” by “alter[ing] the fundamental details of a regulatory scheme in vague terms or ancillary provisions.”[35]
The Organizations vigorously assert that asserting jurisdiction to allow the large-scale leasing of public lands in the manner proposed would be just such an elephant in a mousehole that the Court again has said is unacceptable. It is unfortunate that the Sackett Court application of these basic legal canons reflects a legal position that is well settled. The US Supreme Court has specifically stated this in 1988 as follows:
“In ascertaining the plain meaning of the statute, the court must look at the particular statutory language at issue as well as the language and design of the statute as a whole.”[36]
More than 150 years earlier the US Supreme Court clearly mandated this position as follows:
“The enlightened patriots who framed our constitution and the people who adopted it must be understood to have employed words in their natural sense and to have intended what they have said.”[37]
This long history of Courts requiring clear statutory authority for agency action is a basic canon of statutory interpretation, so we must question why such an issue was not addressed in the Proposal. Failing to provide basic information negatively impacts the publics’ ability to understand what is being proposed and how it relates to existing planning and statutory authority. We submit this type of a conceptual problem is why we are asking for a larger engagement be performed around the development and implementation of the use of the conservation lease on public lands managed for multiple uses. We are also asking for this engagement to occur before any site-specific planning to ensure that the tools provided for site specific planning can equitably and accurately benefit all parties functioning in this area. This is simply an unprecedented usage of these lands and could impact many interests. Once issues such as this are resolved we can see no reason why conservation lease concept would not receive Congressional authorization.
3(d). Conservation leases cannot obstruct existing legal usages.
The proper application of existing legal and statutory authority is critical to mitigating unintended impacts from the Proposal, as the Proposal states conservation leases can stop existing legal activities on the ground. The Proposal also provides no process to address if closures are even necessary as part of any conservation effort. A vigorous and thorough public process is critical to identifying interests in the area that must be addressed in planning. Engaging partners on basic questions such as the necessity of closures for a project or how the project would minimize restrictions and closures are simply never addressed. Under the Proposal, parties that could be injured by illegal closures do not even have clearly identified statutory process to seek a remedy to this type of issue available to them. Collaboration prior to a conservation effort should address how the public and partners are engaged on these issues must be clearly and directly provided for. They have not been.
Moving forward with implementation of the Proposal without clear guidance on issues like legal public access could have disastrous impacts on existing partnerships and economic benefits that flow to local communities from recreation. Negotiations on foundational positions such as who monitors lease holder activity can be very heavy burdens on local groups that are largely volunteer and involvement can be heavily impacted by basic issues such as the timing of meetings. Most volunteer lead groups are led by members of the public that work traditional jobs and could not attend collaborative meetings during the day. This type of indirect impact from the Proposal is unacceptable. Rather than providing meaningful analysis of possible impacts to existing legal usages many possible impacts are simply not valued at all in the Proposal. What the Proposal would summarize as “causal usage” of legal roads and trails in an area that may be leased for conservation are often highly valued recreational opportunities on public lands that have been through numerous rounds of NEPA analysis. This is another example of an elephant trying to be hidden in a mouse hole in the planning process.
The Organizations vigorously assert that the Proposal must clearly and directly address how BLM will ensure that any closure is the minimal amount needed to achieve the goals of the RMP, recognize the existing NEPA analysis and in balance with the conservation effort. If a temporary closure is necessary, these temporary closures must be identified as the minimum amount necessary to achieve the goals. The Proposal must specifically provide how closures will occur and penalties if the conservation lease holder fails to comply with these requirements. The current Proposal does none of this, and dismisses this concern as a mere casual usage of public lands. The current Proposal would force the public to become the enforcement tool for ensuring that public access is not loss or that lost access is only temporary despite decades of NEPA analysis supporting the existence of the opportunity. This situation will be made worse as the for-profit lease holder of the conservation lease will be comparatively well funded compared to the member of the public seeking to legally use public lands subject to the lease. This is patently unfair to the public and must be addressed and mitigated in the Proposal.
The failure to meaningfully address existing usages allows other significant indirect impacts to be entirely overlooked. Impacts to existing legal uses must be clearly and directly protected against under any regulations seeking to provide access to any public lands, as once the for-profit conservation lease holder is performing conservation activities on the ground there will be a strong economic desire of that leaseholder to continue to operate in a for profit manner. Simply stopping other multiple uses, rather than managing multiple uses will expand profits from any project. The Proposal fails to address this serious concern in any substantive manner with the following provisions:
“The proposed rule would define the term ”casual use” so that, in reference to conservation leases, it would clarify that the existence of a conservation lease would not in and of itself preclude the public from accessing public lands for noncommercial activities such as recreation. Some public lands could be temporarily closed to public access for purposes authorized by conservation leases, such as restoration activities or habitat improvements. However, in general, public lands leased for conservation purposes under the proposed rule would continue to be open to public use.”[38]
These provisions are horribly open ended in scope and fail to address basic questions such as who will monitor temporary closures and ensure lease requirements will be honored. The Proposal fails to mention that these “casual uses” are in fact legal uses of the area that may have been repeatedly found sustainable after multiple rounds of NEPA. These casual users might also be interests that could be partners in conservation efforts. Without clear guidance on how lease credits will be allocated and managed, a new leaseholder would have no reason to engage with other partners in the planning area to ensure that efforts and credits are balanced. Rather the Proposal almost silence on this issue would create a situation where new leaseholders would benefit from not engaging with groups already working on the ground. This concern is only compounded by the fact this concern is addressed in a highly dismissive manner.
Any substantive comment on this issue is complicated by the fact the above provisions are in direct contradiction to provisions of the Proposal immediately following the above section. These subsequent conflicting provisions on this issue provide as follows:
“This provision is not intended to provide a mechanism for precluding other uses, such as grazing, mining, and recreation. Conservation leases should not disturb existing authorizations, valid existing rights, or state or Tribal land use management. Rather, this proposed rule is intended to raise conservation up to be on par with other uses under the principles of multiple use and sustained yield…. Once a conservation lease is issued, § 6102.4(a)(4) would preclude the BLM, subject to valid existing rights and applicable law, from authorizing other uses of the leased lands that are inconsistent with the authorized conservation use.”[39]
The Organizations are very concerned that the above provisions are almost completely contradictory and are also highly flexible and subjective as many of the terms are poorly defined and are often taking rather unique interpretations of existing definitions. The Organizations are very concerned that the open-ended nature of the standards will cause long term confusion and conflict, such as those that continue to plague the discussion of possible Wilderness Study Areas. WSA management problems persist almost 50 years after inventory was completed by land managers and found sufficient and complete by Congress. Even though many areas were never found suitable for inclusion as Wilderness, in some cases due to high levels of casual usage of motorized usage on these lands, management efforts still continue to try and move these areas into Wilderness type designations.
It is disappointing that the Proposal fails to value decades of analysis, efforts and partnerships, instead choosing to avoid addressing these previous efforts and this failure will cause conflicts to simply explode in size and intensity. These types of management challenges are exactly the type of problem that the Supreme Court found to result from managers attempting to jam elephants into mouseholes. The Organizations are very concerned that WSA will be hotspot areas for conservation and there are some WSA that have large amounts of motorized usage on them. We would like to resolve WSA conflicts rather than make them worse. The Organizations are also concerned that implementation of these rather open ended and ambiguous requirements for conservation leasing will lead to significant new conflicts.
3(e). Conservation leases should never create presumptions for future management standards.
The Organizations are very concerned that in numerous locations the Proposal appears to seek to tie future management decisions to protect areas to the existence of a conservation lease at some time previously. This makes absolutely no sense as conservation leases could be occurring in areas protected, possibly by Congressional actions, for a range of multiple uses, not just conservation. Again, this is an elephant of an issue trying to be hid in a mousehole. One such provision would be as follows:
“The proposed rule would define the term ”disturbance” to provide the BLM with guidance in identifying and assessing impacts to ecosystems, restoring affected public lands, and minimizing and mitigating future impacts.”[40]
The Organizations would be VERY concerned if any conservation lease was thought to set a precedent to any specific level or type of management in the future. As the Organizations have noted there are a significant number of projects and efforts undertaken by our community that could be suitable to award some type of credit towards. We can envision conservation-based credits being provided on a wide range of land management prescriptions and at no point should the mere existence of a conservation lease create a presumption of any future management prescription. This type of decision making is horribly pre-decisional and would allow managers in the future to completely avoid NEPA analysis of impacts and benefits from decisions that are being made.
The Organizations are compelled to address this type of a concern as we continue to struggle with the management of many previous inventory efforts and processes, such as Wilderness Study areas and USFS Roadless Areas on USFS lands. These are an inventory of characteristics of these areas and not a management standard but we continue to hear calls for these areas to be managed as Wilderness despite many of the areas never being suitable for designation. These challenges exist despite numerous locations in the Wilderness Act clearly stating that the mere inventory of these areas does not remove the multiple use mandate for the area until Congress designates the area or releases the areas. Planners must avoid challenges such as this moving forward rather than making the same mistakes again, and this is a concern as the Proposal has no provisions to avoid this type of impact but rather appears to encourage this type of management.
3(f). Portions of the Proposal seek to apply new management standards without mentioning multiple uses.
The systemic failure of the Proposal to provide detailed discussions of how existing successes and partners and how existing multiple use decisions and mandates would be integrated into new efforts numerous provisions in the Proposal is disappointing. This is a stark contrast to the USFS sustainability proposals that are currently open for public comment at the same time as the BLM. The USFS identifies multiple use management and partnerships in some detail throughout their Proposal, which only highlights the silence of the BLM Proposal. The BLM Proposal fails to recognize multiple uses in any way at all and continues to speak of conservation in complete isolation, as exemplified in the guidance as follows:
“Section 6103.1–1—Land Health Standards and Guidelines Proposed § 6103.1–1 would instruct authorized officers to implement land health standards and guidelines that conform to the fundamentals of land health across all lands and program areas. This includes reviewing land health standards and guidelines during the land use planning process and developing new or revising existing land health standards and guidelines as necessary, and periodically reviewing land health standards and guidelines in conjunction with regular land use plan evaluations. Until the authorized officer has an opportunity to review and update land health standards and guidelines through land use planning processes, § 6103.1–1(a)(1) of the proposed rule would direct authorized officers to apply existing land health standards and guidelines, including those previously established under subpart 4180 of the agency’s grazing regulations fundamentals of rangeland health), across all lands and program areas.
Proposed § 6103.1–1(b) through (d) would require the authorized officer to establish goals, objectives, and success indicators to ensure that each land health standard can be measured against resource conditions and to periodically review authorized uses for consistency with the fundamentals of land health. Once land health standards and guidelines are established, any action in response to not meeting them would be subject to § 6103.1–2(e)(2) and taken in a manner that takes into account existing uses and authorizations. Under the proposed rule, the BLM may establish national indicators in support of the implementation of the fundamentals of land health.”[41]
The Organizations are simply astonished that multiple uses or existing planning or Congressional designations are simply are never even mentioned in the development and application of these standards. The Organizations are very concerned that the above provisions again represent a direct and material conflict between these provisions and other portions of the Proposal seeking input on how leases should be developed and lengths of time for leases and bonding requirements. These questions are moot if the entire process is simply going to be applied. The conflict that will result from these basic failures will be immense and result in no benefit reaching the ground. Again, this issue is another elephant trying to hide in a mousehole.
4. NEPA analysis provided is facially insufficient and results in a fragmented method of plan development.
The NEPA analysis of the Proposal must be significantly expanded to achieve basic legal sufficiency, as this Proposal is proceeding under just a categorical exclusion violates both NEPA and internal guidance documents of the BLM. The Organizations submit that the experiences of the USFS with the development of their 2012 planning rule are highly relevant to our concerns about the lack of NEPA analysis being undertaken by the BLM. The USFS sought to coordinate their efforts and undertake a complete EIS of the new rule and its impacts and the Organizations submit this vigorous NEPA process was critical to the development of a Rule that has largely been successful on the ground and mitigated unintended impacts.
Rather than consolidate all issues into a single location and align efforts and analysis to avoid unintended impacts, BLM has chosen to divide their planning efforts into numerous concepts, each of which are being treated separately. It has been our experience that management development based on these types of standards fails to address issues on the ground or translate into long term success. Often these isolated management efforts and concepts are poorly defined and overlap other efforts in terms of scope and alignment. Basic good management strategies require the cumulative impacts of these numerous isolated efforts must be reviewed and streamlined as most decisions will be made under multiple overlapping standards. This factual conclusion results in identification of the relationships of these standards to each other which is critical in developing an effective decision-making process. An efficient effective process will also foster better relationships with partners, as partners will not be forced to attend repetitive meetings or discussions to address similar issues.
Not only is the failure to seek some type of clearly defined goals and objectives poor management decision making any assertion the Proposal may continue forward with just a Categorical Exclusion and comply with NEPA planning requirements is internally inconsistent with landscape target of the goals and objectives of the Proposal. The large-scale changes that are sought to be applied throughout the planning process are not even address in the NEPA provisions of the rulemaking, which the Proposal outlines as follows:
“The BLM intends to apply the Department Categorical Exclusion (CX) at 43 CFR 46.210(i) to comply with the National Environmental Policy Act. This CX covers policies, directives, regulations, and guidelines that are of an administrative, financial, legal, technical, or procedural nature or whose environmental effects are too broad, speculative, or conjectural to lend themselves to meaningful analysis and will later be subject to the NEPA process, either collectively or case-by case. The BLM plans to document the applicability of the CX concurrently with development of the final rule.”[42]
Any assertion that a Categorical Exclusion is sufficient NEPA analysis to support the effort is in direct contradiction to the target scale of the Proposal which is outlined as follows:
“To ensure that health and resilience, the proposed rule provides that the BLM will protect intact landscapes, restore degraded habitat, and make wise management decisions based on science and data. To support these activities, the proposed rule would apply land health standards to all BLM-managed public lands and uses, clarify that conservation is a ”use” within FLPMA’s multiple-use framework, and revise existing regulations to better meet FLPMA’s requirement that the BLM prioritize designating and protecting Areas of Critical Environmental Concern (ACECs). The proposed rule would add to provide an overarching framework for multiple BLM programs to promote ecosystem resilience on public lands.”[43]
The inherent conflict of the determination the new regulations created by Proposal may proceed with only a Categorical Exclusion is immediately apparent when the goals and objectives of the Proposal are compared to existing guidance documents from the BLM on the necessity to prepare an EIS. These internal BLM guidance documents provide as follows:
“11.8 Major Actions Requiring an EIS.
-
- An EIS level analysis should be completed when an action meets either of the two following criteria.
(1) If the impacts of a proposed action are expected to be significant; or
(2) In circumstances where a proposed action is directly related to another action(s), and cumulatively the effects of the actions taken together would be significant, even if the effects of the actions taken separately would not be significant,”[44]
The Organizations submit that these landscape level goals can only be achieved through a significant change in landscape level planning, and when the cumulative impacts of these landscape level change, the need for expanded NEPA analysis becomes immediately apparent. These levels of planning would basically be entirely new and would have a significant impact on a wide range of issues. The lack of factual basis in the BLM position that the Proposal can move forward without an EIS level of analysis is clear when the cumulative impacts of all the separate planning efforts (Renewable Energy, species, recreation) are consolidated.
The Organizations also submit that the position of the BLM that only a Categorical Exclusion under NEPA is necessary to undertake a complete review of their planning rule is simply insulting to partners of all types. It has been the Organizations experience that even small projects or permits, including club rides that occur on existing resources require at least an Environmental Assessment. Many of the partners now alleged to be sought to engaged are involved in multi-year EA type analysis on a wide range of issues have been consistently told the EA process is the minimum allowed. Asserting a small trail proposal requires an EA while the complete revision of BLM planning can proceed with a Categorical Exclusion despite the Proposal changing almost very component planning is problematic for many reasons beyond legal requirements. This variable standard of NEPA analysis sends a message to partners and it is not positive. The Organizations submit these differences in NEPA application cannot be overlooked and will do little to foster support or partnership for planning efforts moving forward. Organizations submit everyone must be treated similarly for NEPA purposes.
Again the contrast of the BLM sustainability efforts with USFS sustainability efforts cannot pass without comment as these conclusions cannot be reconciled with USFS determinations regarding the new sustainability and climate change planning rule for the USFS that is much smaller in scale and scope.[45] USFS immediately recognized the cumulative and significant impacts of their sustainability rule and moved forward with a vigorous public input and review process under their existing planning rule which was subjected to a full EIS when it was adopted. Given that the new USFS and BLM Proposals are moving at the same time, and the USFS is a significantly smaller scope effort than BLM Proposal there should be some level of consistency in the agencies NEPA analysis. That consistency is not present currently which indicates a severe issue with the BLM’s determination.
The failure of the Proposal to be subjected to any NEPA review represents a significant failure of the BLM to learn from their previous planning efforts that failed. NEPA issues were a major problem with the BLM 2016 Planning Rule proposal(BLM Planning 2.0) and rather than submitting the current Proposal to higher levels of analysis than previously failed efforts, even less NEPA analysis is provided. BLM Planning 2.0 at least provided their questions to identify how the NEPA level was determined. This Proposal fails to even provide that basic a summary. While there is arguable authority in NEPA for this type of analysis, the previous failures of BLM planning must be addressed and learned from rather than expanded. Given the recent Sackett Supreme Court decision tightening the relationship between authorizing legislation for agencies and planning efforts and the tightening of NEPA requirements in the Fiscal Responsibility Act of 2023,[46] this NEPA determination would appear to be problematic legally at best. This is disappointing. Not only does this Proposal seem destined to legally fail, it also sends a message to partners and that message is not positive at all. This message could do serious damage to existing relationships for a much longer period.
5(a). The Proposal fails to align with United Nations recommended Best Practices in any meaningful way.
The deeply problematic nature of the Proposal’s foundation is compounded even further by the fact the Proposal directly conflicts with United Nations guidance on best available science addressing management and decision making for the creation of conservation credits. Best available science in planning and conservation is reasonably well established as a result of decades of work by the United Nations on this issue. The UN has identified several critical factors in successfully planning to protect resources, which the BLM has largely chosen to ignore in the Proposal. The Organizations believe how these factors are addressed or not addressed in the Proposal provides a good outline of the reasons we are opposing the Proposal. The alignment of the Proposal with successful factors in management are only made more important as the challenges managers are facing are more complex and multifaceted than other examples of conservation credits in the US market.
Our frustration starts from the point that the UN guidance on this issue essentially reflects factors recognized by management and planning experts required in creating successful planning efforts for any issue. These factors are:”
- “Planners need to recognize history of area and previous efforts to avoids repetition and confusion;
- Efforts need clearly defined goals and objectives;
- Consistent and Steady funding; and
- Good community buy in must be achieved.” [47]
The Organizations would agree with these concepts for management of conservation credits as these concepts generally align with a good decision-making process on any issue. This analysis is critical to the success of any management effort and is already required for any BLM effort as BLM planning must be based on best available science. Immediate conflicts with best available science only compound when more specific guidance is reviewed. The United Nations World Conservation Monitoring Center, the lead agency in the conservation credits market for several decades, outlines very similar concerns for governments seeking create conservation credits develop markets as follows:
“Governments can provide regulatory and political certainty to VCM transactions by clarifying the rules of engagement for the VCM in their countries and by explicitly stating that they are ready to support project developers and investors in complying with relevant rules, regulations, and safeguards. The VCM also influences public policy and compliance markets, and in some cases voluntary carbon crediting programs directly interact with government carbon pricing schemes.”[48]
The United Nations continues to outline these types of foundational concerns as follows:
Two key intertwined issues are land access and carbon rights, said Timon Rutten, Head of Enterprise at Rewilding Europe. Accessing and aggregating sufficient land for a project can be complex and time consuming, and often results in the project being carried out on land with multiple owners. Once land is secured, there is still the issue of the carbon rights: who owns them and how to split the income across owners. This is why initiating projects is incredibly complicated. Projects also need to determine who they are willing to sell credits to, on what terms, and to be ready when companies approach them.[49]
These generalized management concerns have been more fully integrated into the development of conservation credit efforts as follows:
“Here sustainable development is defined as “development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs” (International Institute for Sustainable Development, 2017). There are three key aspects to sustainable development that must be considered in balance to ensure that natural values (biodiversity, ecosystem services and ecosystem function) are not compromised: environmental, social and economic (Gibson, 2009; Moldan & Dahl, 2007; International Institute for Sustainable Development, 2017; Macintosh, 2015)…. While much has been written on the design of biodiversity offsets (Bull, Suttle, Gordon, Singh & Milner-Gulland, 2013; Carreras Gamarra, Lassoie, & Milder, 2018; Gardner et al., 2013; Quétier & Lavorel, 2011), this previous work has predominantly focused on the environment, excluding the social (Bidaud, Schreckenberg, & Jones, 2018; Gibbons, Macintosh, Constable and Hayashi, 2018; Githiru et al., 2015; Jacob, Buffard, Pioch & Thorin, 2017; Macintosh, 2015; Nijnik & Miller, 2017; Scholte, van Zanten, Verburg & van Teeffelen, 2016; Takacs, 2018) and/or economic (Benabou, 2014; Fallding, 2014; Jacob et al., 2017) aspects of sustainability, leading to inequalities and an inconsistent approach (Abdo et al., 2019; Jacob et al., 2017). Therefore, to ensure biodiversity offset requirements compensate for all aspects of sustainable development, a holistic model, incorporating natural values for design, implementation and ‘end-of-life’ phases, is needed. In particular, biodiversity offsets should address the Sustainable Development Goals that provide “strategies that build economic growth and address a range of social needs including education, health, social protection, and job opportunities, while tackling climate change and environmental protection” (United Nations, 2019).”[50]
Researchers expand on the United Nations concerns for the entire model to be based on best available science, by addressing the factors necessary for a conservation credit market to successfully function as follows:
“Habitat restoration biodiversity offsets rely on conservation activities that improve habitat quality and/or extent as a compensatory measure (Maron, 2012; McDonald et al., 2016). Habitat restoration biodiversity offsets should only be implemented where natural values can be explicitly defined, there is sound scientific evidence that restoration will be successful, and time lags and uncertainties are effectively accounted for (Maron et al., 2012). Habitat restoration offsets can ensure no net loss (Maron & Louis, 2018) but have been shown to have unpredictable costs and a lower likelihood of success.”
The Organizations are very concerned that the three general characteristics of a successful credit program are not addressed in the Proposal but rather they are entirely avoided. Even asserting there is general alignment is problematic factually. These foundational alignment issues for the Proposal’s scientific validity are troubling as the BLM’s need to manage in compliance with research is specifically identified as a major concern for the BLM moving forward in their science policy, various Executive Orders and numerous NEPA and Administrative Procedures Act requirements.
5(b). In addition to the Proposal failing to address UN science recommendations, the Proposal also fails to apply the BLM science strategy.
The United Nations has provided a large amount of information and guidance for those interests who are seeking to create a conservation credit type program, which while not legally binding is highly relevant to development of a conservation credit type market. This type of weighty information has always been identified as important by the BLM 2008 Science Strategy, which states:
“In this era of rapidly expanding knowledge and methodologies of predicting future environmental changes, it is critical to keep up with the state of knowledge in resource management. By making use of the most up-to-date and accurate science and technology and working with scientific and technical experts of other organizations, we will be able to do the best job of managing the land for its environmental, scientific, social, and economic benefits.” [51]
The need to accurately understand what resources are available, what resources need to be developed and the integration of these resources is again highlighted as critically important to successful planning. The role that strategic planning documents play in determining current resources available and in identifying those resources that need to be developed is specifically and extensively discussed in the provisions of the 2008 BLM Science Strategy. This discussion specifically identifies:
“National management issues will be focused to reflect how they apply to the various biogeographic regions of the United States. The BLM identifies and prioritizes the science needs and problems that threaten the targets and goals from the National Strategy. Targets are established for managing specific goals or objectives……The science needed to address the regional management issues will be defined. Science may include existing resource inventory, monitoring, and other data, as well as new information derived from research and project efforts.”[52]
Similar sentiments are expressed in a wide range of BLM planning efforts such as the NLCS and others.[53] The Organizations are very concerned these factors and issues are never mentioned with any specificity in the Proposal and Rules. Basic guidance or vision is not provided on rudimentary issues such as who may or may not be eligible for conservation credit, who would provide credits and who would benefits be maintained in the long run. This is very concerning and we must ask if these standards and criteria of success are not addressed in the Rule, where will they be developed and applied? The Organizations are VERY concerned that without basic guidance around how conservation credits are going to be created and managed there will be a huge amount of unnecessary conflict between interests and this must be avoided. These concerns expand greatly when the introduction of expanded use of the ACEC designation process is incorporated into the proposed leasing development.
6(a). Executive Orders requiring an expansion of recreational opportunities issued by President Biden must be accurately addressed in the Proposal.
Our concerns around the numerous actions by Congress have directly targeted landscape level planning requirements that are not accurately summarized or entirely overlooked in the Proposal, are addressed previously. These concerns extend to various Executive Orders, several of which have been issued and refined by numerous administrations. While some Executive Orders may have been in place for more than 50 years, and as a result might be more easily excused for not being analyzed, many Executive Orders issued by President Biden are mentioned but in a woefully inaccurate manner. The recent issuance of Executive Order # 14008 by President Biden on January 27, 2021 would be an example of a decision that is partially and woefully inaccurately summarized in the Proposal. According to the Proposal EO14008 requires the following:
“Executive Order 14008: Tackling the Climate Crisis at Home and Abroad calls for quick action to build resilience against the impacts of climate change, bolster adaptation, and increase resilience across all operations, programs, assets, and mission responsibilities with a focus on the most pressing climate vulnerabilities. Section 211 of Executive Order 14008, calls on Federal agencies to develop a Climate Action Plan.”[54]
The Organizations do not contest that a climate action plan is a portion of this EO, but the EO spans more than 27 pages and addresses a wide range of other topics that must also be addressed as part of this effort. These other factors simply are ignored in the Proposal, as exemplified by the fact that EO14008 specifically addresses the requirement of expanding recreational access and economic benefits FIVE DIFFERENT TIMES in the EO. §214 of EO 14008 clearly mandates improved recreational access to public lands through management as follows:
“It is the policy of my Administration to put a new generation of Americans to work conserving our public lands and waters. The Federal Government must protect America’s natural treasures, increase reforestation, improve access to recreation, and increase resilience to wildfires and storms, while creating well-paying union jobs for more Americans, including more opportunities for women and people of color in occupations where they are underrepresented.”
The clear and concise mandate of the EO to improve recreational access to public lands is again repeated in §215 of the EO as follows:
“The initiative shall aim to conserve and restore public lands and waters, bolster community resilience, increase reforestation, increase carbon sequestration in the agricultural sector, protect biodiversity, improve access to recreation, and address the changing climate.”
217 of EO 14008 also clearly requires improvement of economic contributions from recreation on public lands as follows:
“Plugging leaks in oil and gas wells and reclaiming abandoned mine land can create well-paying union jobs in coal, oil, and gas communities while restoring natural assets, revitalizing recreation economies, and curbing methane emissions.”
There is significant concern raised around the 30 by 30 concept and climate plans that are memorialized in EO 14008 in the Proposal. While the EO does not define what “protected” means, the EO also provided clear and extensive guidance on other values to be balanced with. From our perspective the fact that large tracts of land are Congressionally designated or managed pursuant to Executive Order far exceeds any goals for the EO. While there are overlap between these categories that precludes simply adding these classifications together, this also does not alter the fact the planning area has achieved these goals of 30% of acreages being protected.
Unfortunately, this is not the only time that new Executive Orders issued by President Biden are not accurately summarized in the Proposal. EO 14072 is also referenced numerous times in the Proposal and again the Proposal fails to reflect the scope and intent of this Order, and again this EO specifically recognizes and protects recreational usages as follows:
“Section 1. Policy. Strengthening America’s forests, which are home to cherished expanses of mature and old-growth forests on Federal lands, is critical to the health, prosperity, and resilience of our communities….We go to these special places to hike, camp, hunt, fish, and engage in recreation that revitalizes our souls and connects us to history and nature. Many local economies thrive because of these outdoor and forest management activities, including in the sustainable forest product sector.”[55]
EO 14072 specifically addresses recreational issues and opportunities as a factor to be addressed in the planning process as follows:
“Sec. 2. Restoring and Conserving the Nation’s Forests, Including Mature and Old-Growth Forests. My Administration will manage forests on Federal lands, which include many mature and old-growth forests, to promote their continued health and resilience; retain and enhance carbon storage; conserve biodiversity; mitigate the risk of wildfires; enhance climate resilience; enable subsistence and cultural uses; provide outdoor recreational opportunities; and promote sustainable local economic development….”[56]
EO 14072 continues to recognize the need to protect recreational access and related economic benefits as follows:
“(d) The Secretaries, in coordination with the heads of other agencies as appropriate, shall within 1 year of the date of this order: (iii) develop, in coordination with the Secretary of Commerce, with State, local, Tribal, and territorial governments, and with the private sector, nonprofit organizations, labor unions, and the scientific community, recommendations for community-led local and regional economic development opportunities to create and sustain jobs in the sustainable forest product sector, including innovative materials, and in outdoor recreation, while supporting healthy, sustainably managed forests in timber communities.”[57]
While the Proposal does a slightly better job in capturing the scope of the EO, it falls well short of capturing the entire EO and then applying it in the Proposal. The Proposal summary is as follows:
“Executive Order 14072, Strengthening the Nation’s Forests, Communities, and Local Economies, recognizes that healthy forests are ”critical to the health, prosperity, and resilience of our communities.” It states a policy to pursue science-based, sustainable forest and land management; conserve America’s mature and old-growth forests on Federal lands; invest in forest health and restoration; support indigenous traditional ecological knowledge and cultural and subsistence practices; honor Tribal treaty rights; and deploy climate-smart forestry practices and other nature-based solutions to improve the resilience of our lands, waters, wildlife, and communities in the face of increasing disturbances and chronic stress arising from climate impacts.”[58]
These horribly inaccurate summaries of Executive Orders provided in the Proposal will be huge impediments to implementing any of the Proposal, as the entire effort will be starting from a position of mistrust with the public. After a review of the Proposal, not able to identify any portion of the Proposal that might comply with the requirements of EO 14072 or EO 14008. The public should not be required to review every document referenced in a Proposal of this scale to ensure that the provisions of the regulations or Executive Orders are at least accurately summarized. This is disappointing to say the least.
6(b). How will sufficient resources and staffing within the Agency be achieved to support new effort in compliance with EO 12866 and EO 13563?
The failure to meaningfully analyze issues will compound existing shortfalls of staffing and resources and resolving these will be critical to the implementation of the Proposal. Concerns such as this have driven several Executive Orders seeking to improve regulation and regulatory review processes, including EO 12866 Issued by President Clinton in 1993 and reaffirmed by President Obama with the issuance of EO 13563 and again reaffirmed with President Bidens memo issued January 20, 2021.
The 5 specific requirements of this family of Executive Orders and memos is summarized as follows in the EO 13563:
“This order is supplemental to and reaffirms the principles, structures, and definitions governing contemporary regulatory review that were established in Executive Order 12866 of September 30, 1993. As stated in that Executive Order and to the extent permitted by law, each agency must, among other things: (1) propose or adopt a regulation only upon a reasoned determination that its benefits justify its costs (recognizing that some benefits and costs are difficult to quantify); (2) tailor its regulations to impose the least burden on society, consistent with obtaining regulatory objectives, taking into account, among other things, and to the extent practicable, the costs of cumulative regulations; (3) select, in choosing among alternative regulatory approaches, those approaches that maximize net benefits (including potential economic, environmental, public health and safety, and other advantages; distributive impacts; and equity); (4) to the extent feasible, specify performance objectives, rather than specifying the behavior or manner of compliance that regulated entities must adopt; and (5) identify and assess available alternatives to direct regulation, including providing economic incentives to encourage the desired behavior, such as user fees or marketable permits, or providing information upon which choices can be made by the public.”[59]
The applicability of the requirements of this family of Executive Orders was reaffirmed with the issuance of a Presidential Memo from President Biden on January 20, 2021.[60] President Biden’s Memo specifically provides as follows:
“These recommendations should provide concrete suggestions on how the regulatory review process can promote public health and safety, economic growth, social welfare, racial justice, environmental stewardship, human dignity, equity, and the interests of future generations. The recommendations should also include proposals that would ensure that regulatory review serves as a tool to affirmatively promote regulations that advance these values. These recommendations should be informed by public engagement with relevant stakeholders.
(b) In particular, the recommendations should:…
(ii) propose procedures that take into account the distributional consequences of regulations, including as part of any quantitative or qualitative analysis of the costs and benefits of regulations, to ensure that regulatory initiatives appropriately benefit and do not inappropriately burden disadvantaged, vulnerable, or marginalized communities;”
Given that these EO specifically addresses the use of marketable permits and economic incentives as tools to be analyzed for possible impacts and benefits, the Organizations must question why the Proposal fails to recognize and analyze factors such costs and benefits and integration of the new regulatory process into existing processes. This memo only compounds the failure of the Proposal to undertake a cost benefit analysis in its development, as the economic analysis provide with the Proposal is woefully inadequate as outlined in other portions of these comments.
The impacts of cumulative regulations from the Proposal could be immense and again must be addressed and minimized but again has been omitted. In many areas of the country, our voluntary grant funded projects include the issuance of direct subsidy type grants to BLM offices to hire staff to support basic recreational management. This partnership model has resulted from the fact that no partner of a land manager is able to perform work on public lands without some type of oversight. In many BLM Offices there are years of recreational projects that have been approved by NEPA that we simply cannot complete as the BLM lacks staff to sign paperwork or oversee partner efforts. If we hire a contractor to perform work entirely outside BLM for NEPA efforts, NEPA compliance still must be proven, status meetings must occur, approval meetings and sign offs must also occur. That oversight requires BLM staff. Even with the direct subsidization of the hiring of staff, many offices we work with are still unable to hire sufficient staff to support our programs. In most areas, agency salaries simply are not able to provide a competitive wage, even if we subsidize them. As a result, our Organizations are looking at moving to permanent seasonal roles to streamline hiring or moving to a wage/grade model of compensation for some positions. These are efforts that will not be streamlined with new planning requirements being imposed that lack funding and a method to hire staff necessary to implement the effort. Without these resources, existing issues will continue to stall and these are the indirect impacts that must be addressed in the Proposal.
The unreasonably narrow view of the impacts from the Proposal has resulted in the significant expansions of burdens on existing staffing and resources being totally overlooked. Certainly, conservation leases and ACEC development will require cultural resource inventories, public meetings and Section 7 consultations for ESA compliance. Even if there is minimal on the ground work being done as a result of conservation credit leases, there will still be a significantly increased need for agency staff. This type of operational requirement will significantly increase if there are actual mitigation projects occurring on the ground or the recreational improvement projects that we are already having to wait far too long to complete. Failing to address these types of on the ground challenges for offices who are working in the Conservation Credit area or review of ACEC proposal that were previously declined will be critical to the success of this effort. Not only is this critical to the success of this project it is critical to ensuring that other partner efforts are not stopped or significantly slowed as a result of staffing issues. We are aware of this type of problem arising in several offices and this situation resulted in massive conflicts between land managers and users. These types of failures must be addressed clearly and directly before this model is moved forward with.
The Organizations are intimately aware of the large upfront costs that must be covered in the development of any large-scale planning effort, and as a result would ask to understand how these costs are going to be covered during the planning process? Regardless of the process that is finally determined to be applicable to the development of a conservation credit program or identifying areas that might be available for conservation leases or expansion of ACEC designations, significant restructuring of existing RMP or development of updated RMP will be necessary. This could easily take decades to develop and allowing existing projects to stall for this period of time is completely unacceptable to us. Each of these paths forward provide immense challenges that simply are never addressed in the Proposal. If the agency undertakes funding these efforts, how will these efforts be aligned with existing management efforts on the ground? If a third party undertakes these inventories, how will the accuracy of these inventories be assured?
6(c). The Department of Interior climate action plan addresses recreational access but the Proposal is silent on this issue.
In addition to the failures of the Proposal to accurately summarize numerous statutory and Executive Order requirements, the Proposal also fails to accurately summarize the Department of Interior’s 2021 Climate Action Plan. DOI’s 2021 Climate Action Plan specifically identifies one of the 10 goals of the effort as working collaboratively with partners as follows:
“Build Strong Partnerships. Adaptation strategies will be collaborative and coordinated across multiple scales and will build on existing efforts and knowledge of public and private partners, including recreational groups, industry, international counterparts, municipalities, States, Tribes, and Insular areas. The Department’s network will also be expanded to include new partners with diverse views and values.”[61]
While partner collaboratives are clearly identified in the DOI 2021 Climate Action Plan, the Proposal simply fails provide more analysis of this issue beyond a naked assertion of compliance with the Plan. While the Organizations have been a partner of the BLM for decades, we are unaware of any engagement before the Rule was issued and we are unable to find any portion of the Proposal that could provide insight into the partnership moving forward. The implications from these types of failures are immense as the Proposal fails to even recognize possible partners or provide reasonable information to the public to allow for decision making. Analysis failures like this horribly undermines possible partners faith in the process and as a result future partners that will be hesitant to engage with managers. This also exemplifies why a Categorical Exclusion is totally insufficient for NEPA analysis as this issue is another elephant in a mousehole that the Supreme Court has expressed serious concerns over.
7. Possible conflict between the Proposal and new USFS initiatives ramping up timber harvests must be recognized and analyzed.
The almost immediate irreconcilable conflict of the current BLM planning initiative, which seeks to protect large intact landscapes, with current US Forest Service efforts, which seek to greatly expand the management of timber resources and create healthy forests cannot be overlooked.
Even on basic issues such as the definition of disturbance, the alignment of these efforts appears to be non-existent. The USFS is seeking to expand timber production and active management in a response to natural disturbances, such as fire and invasive species, while the BLM appears to be going the exact opposite direction by protecting intact landscapes.
The Forest Service sustainability proposal provides the following summary of their intent and direction: [62]
The direct conflict between what USFS is proposing and the direction that BLM is pursuing is could not be in more direct conflict as USFS is seeking to streamline their management process to allow for more efficient management of resources. BLM seeks to expand the use of highly restrictive management designations such as ACEC’s to protect resources. This conflict will become hugely problematic on lands where the agencies are managing adjacent lands on a landscape. USFS effort may increase the disturbance of these lands at significant levels to respond to poor forest health and BLM may be calculating USFS management as a degradation of the landscape and the reason for expansion of restrictive management standards. We truly hope this is not the case but given the BLM proposal foundation problems, this situation could certainly result. Again, this provides another direct example of the insufficiency of the analysis provided in the Proposal. Conflicts such as this are the reason that numerous Executive Orders have been provided that require agencies to align efforts and avoid repetition and to review costs and benefits of their efforts.
8(a). The economic analysis provided with the Proposal is completely insufficient.
The systemic failure to meaningfully analyze issues and possible challenges involved in the implementation of the new management model has resulted in conclusions in the economic analysis that make absolutely no sense at all. The economic analysis provided is horribly conclusory in nature and fails to address much of the information that we have referenced here. Assertions that the economic impact of the effort will be less than $100m annually simply does not align in any way with Naturevest assertions that their involvement in the conservation credit market has resulted in more than $2.5 billion in spending over the last decade or our estimates of similar types of contributions from our voluntary registration program.
As previously outlined in multiple portions of the comments the economic benefits and costs of any effort must be analyzed in the rulemaking effort. Best available science also requires that economic impacts from the conservation efforts must be meaningfully addressed. This type of analysis simply is not provided at all in the Proposal. For example, at no point can we find basic information such as an estimated value for credits that could be in the conservation leasing process, the total value of current conservation credit trading market, how many credits might be expected from this new initiative, cash benefit to land managers from this new program, and estimated costs of running the program to name a few. Understanding the possible overlap of all these planning efforts is specifically and repeatedly required. It is disappointing that more economic information is provided in these comments than is available to the public for review in the Proposal.
The legal insufficiency of what is provided as an economic analysis is evidenced by the fact these provisions require an analysis to determine if the act is or is not applicable. The statutory requirements are clear and provide as follows:
“(a)When an agency promulgates a final rule under section 553 of this title, after being required by that section or any other law to publish a general notice of proposed rulemaking, or promulgates a final interpretative rule involving the internal revenue laws of the United States as described in section 603(a), the agency shall prepare a final regulatory flexibility analysis. Each final regulatory flexibility analysis shall contain—
(1) a statement of the need for, and objectives of, the rule;
(2) a statement of the significant issues raised by the public comments in response to the initial regulatory flexibility analysis, a statement of the assessment of the agency of such issues, and a statement of any changes made in the proposed rule as a result of such comments;
(3) the response of the agency to any comments filed by the Chief Counsel for Advocacy of the Small Business Administration in response to the proposed rule, and a detailed statement of any change made to the proposed rule in the final rule as a result of the comments;
(4) a description of and an estimate of the number of small entities to which the rule will apply or an explanation of why no such estimate is available;
(5) a description of the projected reporting, recordkeeping and other compliance requirements of the rule, including an estimate of the classes of small entities which will be subject to the requirement and the type of professional skills necessary for preparation of the report or record;
(6) a description of the steps the agency has taken to minimize the significant economic impact on small entities consistent with the stated objectives of applicable statutes, including a statement of the factual, policy, and legal reasons for selecting the alternative adopted in the final rule and why each one of the other significant alternatives to the rule considered by the agency which affect the impact on small entities was rejected; and
(6) for a covered agency, as defined in section 609(d)(2), a description of the steps the agency has taken to minimize any additional cost of credit for small entities.”[63]
Given the Federal Administrative Procedure act lays out these factors with some detail would logically lead to the conclusion that these factors would be addressed in some detail in the decision to move further into the economic analysis discussion and analysis. Again, this did not happen.
The Proposal unsupported assertion that its economic conclusions are accurate and do not warrant further analysis fails to comply with APA requirements. This failure becomes only more evident when the standards applied by Courts reviewing administrative procedure act requirements for rulemaking are reviewed. Courts reviewing an agency’s rulemaking authority have clearly stated their review of APA decisions as follows:
“But in cases of great technological complexity, the best way for courts to guard against unreasonable or erroneous administrative decisions is not for the judges themselves to scrutinize the technical merits of each decision. Rather, it is to establish a decision-making process which assures a reasoned decision that can be held up to the scrutiny of the scientific community and the public.”[64]
The Proposal cursory decision making and naked assertions of compliance falls well short of the assurance that a reasoned decision has been made. The unsupported assertion these requirements are not applicable is at best self-serving and insulting to the public the Proposal is seeking to engage with. Allowing this type of unsupported assertion of compliance to satisfy rulemaking requirements would render the federal administrative procedure act is entirely inapplicable.
8(b). Every Executive Order cited in the Proposal specifically requires additional economic analysis of benefits but none is provided.
As the Organizations have noted previously in these comments, the Biden Administration has issued numerous Executive Orders and Presidential Memos that have required the growth of economic benefits from recreation while balancing these benefits with the protection and conservation of resources. These Executive Orders build on the requirements reaffirmed by the administration memo issued January 20, 2021 of the requirements of EO 12866 and EO 13563 which also require significant review of economic costs and benefits of any proposed regulation. Clearly compliance with these Executive Orders requires more than a bare minimum of analysis under the Regulatory Flexibility Act and Administrative Procedures Act. The provided economic analysis is wholly insufficient to begin to address how these benefits to local communities are provided from the Proposal.
8(c). The economic contribution of motorized recreation is overwhelming for communities.
The need to balance various uses on federal public lands pursuant to the multiple use mandate requirements is driven by the large economic contributions that are already provided from these various uses. Localized NEPA analysis has been in place on most federal public lands and these local efforts have balanced benefits from these uses with conservation interests through the development of resource management plans for these lands. This balance must also be addressed in the Proposal at the national level.
The Department of Commerce research through their Bureau of Economic Analysis(BEA) continues to identify the significant contribution of outdoor recreation to the US economy and the overwhelming portion of outdoor recreation that would be classified as motorized for management purposes. The BEA research identified that outdoor recreation accounted for 2% of the GDP or more than $454 Billion in spending annually and that this value was steadily increasing since research started. BEA research further concluded that motorized spending was the dominant portion of spending for recreational activity, and almost exceeded all other spending sources combined. BEA research provides the following breakdown of the total recreational spending:
 [65]
[65]
The Organizations submit that a full understanding of this economic contribution and its components is critical to satisfying the full mandates of various Executive Orders driving the planning effort and existing multiple use mandates. Not only is this information critical to these obligations, this balance is critical to the survival of the smaller communities that are commonly found in and around BLM planning areas that no longer have other revenue streams available to them. While the Proposal seeks to expand funding for conservation, the expansion of the conservation activities should not come at the expense of recreational opportunities.
8(c). BLM own economic analysis highlights the critical economic contributions of recreation on BLM lands.
Every year the BLM also provides high level economic analysis from activities on BLM lands, which is released as part of their “Sound Investment” efforts for BLM lands. [66] The sound investment report from BLM for 2022 clearly identifies that recreation on BLM managed lands contributed more than $11 Billion in economic contributions and 76,000 jobs to local communities which is provided with the following graphic:

The Organizations would be remiss if we did not highlight the fact that recreation provides more than 10% of the entire economic contribution from BLM lands to local communities. Nationally recreational activity on BLM lands also contributes approximately 10% of jobs from BLM lands. When these conclusions of economic contributions of recreation are reviewed at the state level, these percentages increase dramatically. For example, recreation on BLM lands in Idaho make up more than 29% of the economic contribution of BLM lands; California recreational activities on BLM contribute more than 26% of the total economic contribution of BLM lands; Recreational activity in Utah makes up more than 27% of the BLM economic contribution; and in Colorado make up 16% of the total BLM economic contribution.
The Organizations vigorously assert that the sheer scale of these largely sustainable contributions to local communities should have warranted detailed analysis and discussion in any landscape planning effort. The addition of multiple Executive Orders from this administration highlighting the need to protect and improve recreational access and economic contributions from recreation to local communities only highlights our frustrations with the complete inadequacy of the economic analysis provided with the Proposal.
Conclusions.
The Organizations must express vigorous opposition to the Conservation and Landscape Health Proposal as the Proposal appears to be more of a jumbled planning wish list to benefit conservation interests than a coherent revision to planning efforts that aligns with multiple uses. This is disappointing as there could be portions of the Proposal that might be of interest for us moving forward, but the analysis and explanation of these concepts is woefully inadequate. The Proposal fails to provide even arguably legal sufficient analysis of the concepts proposed and how they would be integrated with existing efforts and partnerships. Far too often major challenges or questions around alignment of proposed new efforts with existing resources and planning are simply ignored. This is deeply concerning to our interests both as users of public lands and also as possibly the single largest partner working with the BLM currently. After reviewing the Proposal multiple times, we are still unable to determine if the Proposal seeks to create conservation credits or carbon credits, how this relates to proposed expansions of ACEC designations or how any of these new concepts would be integrated into existing planning. Too often information that is provided is contradictory in nature or so vague as to prohibit meaningful public comment.
The Organizations and our partners remain committed to providing high quality recreational resources on federal public lands while protecting resources and would welcome discussions on how to further these goals and objectives with new tools and resources. If you have questions, please feel free to contact Scott Jones, Esq. (518-281-5810 / scott.jones46@yahoo.com), Chad Hixon (719-221-8329 / chad@coloradotpa.org), or Clif Koontz (435-259-8334 / clif@ridewithrespect.org).
Respectfully Submitted,
Scott Jones, Esq.
CSA Executive Director
COHVCO Authorized Representative
Chad Hixon
TPA Executive Director
Marcus Trusty
President – CORE
Sandra Mitchell
Executive Director – IRC
Authorized Representative – ISSA
Clif Koontz
Executive Director
Ride with Respect
Michelle Stevens
Alaska Snowmachine Alliance
Matthew Giltner
Executive Director
Nevada Offroad Association
[1] As an example of these programs: Polaris Trails grants are outlined here: T.R.A.I.L.S. Grant Program Application | Polaris; Yamaha Access Initiative Grants are outlined here, Yamaha Outdoor Access Initiative (yamaha-motor.com); and Ford’s Bronco wild grant program is outlined here Ford Bronco™ Wild Fund
[2] Welcome to the Off-Highway Motor Vehicle Recreation (OHMVR) Division’s Grant Programs (ca.gov)
[3] Colorado summer program is outlined here https://cpw.state.co.us/Documents/Trails/OHVGrantProgramAwards.pdf Colorado winter program is outlined here.
[4] A summary of video of these efforts to date is provided here: OHV Final on Vimeo
[5] See, Proposal at pg. 19590
[6] See, Proposal at pg. 19584
[7] See, Ecological Indicators; Integrating sciences for monitoring, assessment and management; Issue 74 (March 2017)
[8] See, Zhai et al; The emergy of metabolism in different ecosystems under the same environmental conditions in the agro-pastoral ecotone of northern China; Ecological Indicators; Volume 74 March 2017 pg.198 @ pg. 202.
[9] See, LaNotte et al; Ecosystem services classification: A systems ecology perspective of the cascade framework; Ecological Indicators; Volume 74 March 2017 pg392 @ pg. 401.
[10] Conservation Banking | U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service (fws.gov)
[11] See, Proposal @ pg. 19593.
[12] See, Proposal at pg. 19586.
[13] See, Proposal at pg. 19598
[14] See, Proposal at §6101.4
[15] See, Proposal at pg. 1584
[16] See, 16 USC §1532
[17] See, DOI: US Fish and Wildlife Service; Final Rule; Endangered and Threatened Wildlife and Plants; Designation of Experimental Populations; 88 FR 41835 @at pg. 41837.
[18] PUBLIC LAW 103-433—OCT. 31, 1994
[19] Conservation Definition & Meaning – Merriam-Webster
[20] See, Public Law 111-11 §2002
[21] 15-Year Strategy | Bureau of Land Management (blm.gov)
[22] NLCS plan at pg. 3.
[23] See, Proposal at pg. 19584
[24] See, Proposal at pg. 19587
[25] See, Proposal at pg. 19584
[26] See, 43 USC §1701
[27] BLM manual 1603.02 &.03
[28] As an example of this type of provision please see §137 of America’s Outdoor Recreation Act of 2023 (S873)
[29] See, Mendelson et al: How to repair the worlds broken carbon offset markets; Yale Environmental 360; Nov. 18, 2021; See also G Badgley, J Freeman, J Hamman, B Haya, A T Trugman, W R L Anderegg, D Cullenward(2021) “Systematic over-crediting of forest offsets” Carbon Plan; https://carbonplan.org/research/forest-offsets-explainer; Peters et al; Bootleg fire is burning through trees that are already used as carbon offsets; The Bootleg fire is burning through trees that are being used as carbo (fastcompany.com)
[30] See, FHWA; Trails and Resilience; Review of the Role of Trails in Climate Resilience and Emergency Response March 2023 at pg. 8.
[31] Black’s Law Dictionary 6th edition
[32] Black’s Law Dictionary 6th edition
[33] Kristin P. Davis, Julie Heinrichs, Erica Fleishman, Pricila Iranah, Drew E. Bennett, Joel Berger, Liba Pejchar. Strengths and shortcomings of habitat exchange programs for species conservation. Conservation Letters. 2022;15:el2846. https:/ /doi.org/10.1111/conl.12846; see also Drosteet al; A global overview of biodiversity offsetting governance; Journal of Environmental Management; 316 (2022); Epanchin- Neill et al; Private sector conservation under the US Endangered Species Act; a return on investment perspective; Frontiers in Ecology; 2020; see also Abdo; Biodiversity Offsets can be a valuable tool in achieving sustainable development; Journal of sustainable development; Vol 12 No 5; 2019 @pg. 65.
[34] See, 43 CFR 2740.0-5(b)
[35] Sackett; 598 U. S. ____ (2023) slip opinion at pg. 20 internal citations omitted
[36] See, Kmart Corp v. Cartier Inc; 486 US 281 At 291 (1988); See Also; United States v. Boisdoré’s Heirs, 49 U.S. (8 How.) 113, 122 (1850).
[37] See, Gibbons v. Ogden; 22 US (9Wheat) 1, @71 (1824)
[38] See, Proposal at pg. 19588
[39] See, Proposal at pg. 19591
[40] See, Proposal at pg. 19588
[41] See, Proposal at pg. 19592
[42] See, Proposal at pg. 19596.
[43] See, Proposal at pg. 19583.
[44] http://www.blm.gov/wo/st/en/prog/planning/nepa/webguide/departmental_manual/516_dm_chapter_11.html#11-8
[45] See, USDA Forest Service; Organization, Functions, and Procedures; Functions and Procedures; Forest Service Functions; Federal Register /Vol. 88, No. 77 / Friday, April 21, 2023 / Proposed Rules 24497
[46] H.R.3746 – 118th Congress (2023-2024): Fiscal Responsibility Act of 2023 | Congress.gov | Library of Congress
[47] As examples of these ongoing discussions please see, Ostrom et al; “Why Conservation Efforts Often Fail.” Indiana University. ScienceDaily, 20 September 2007. www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2007/09/070918132832.htm; See also Duffy; Nature Crime: How We’re Getting Conservation Wrong; Yale University Press; Illustrated edition (August 31, 2010); See also; Emerson et al; 7 Reasons why change management strategies fail and how to avoid them; Harvard Division of Continuing Education; Nov 18, 2022. A complete version of the article is available here: 7 Reasons Why Change Management Strategies Fail and How to Avoid Them – Professional Development | Harvard DCE
[48] See, Navigating the complex world of carbon markets: the path to high-quality credits for ecosystem restoration – UNEP-WCMC citing The Voluntary Carbon Markey Explained; September 2021
[49] See, United Nations News August 2022 Beyond greenwashing: understanding the challenges, ambition and potential of carbon trading – UNEP-WCMC
[50] Abdo, L.J., Kemp, A., Coupland, G., and Griffin, S. (2019) Biodiversity offsets can be a valuable tool in achieving sustainable development: Developing a holistic model for biodiversity offsets that incorporates environmental, social and economic aspects of sustainable development. Journal of Sustainable Development, 12(5). doi: 10.5539/jsd.v12n5p65
[51] BLM Science Strategy 2008 – Doc Id BLM/RS/PL-00/001+1700 at pg. iv.
[52] Id at 16.
[53] Science in BLM | Bureau of Land Management
[54] See, Proposal at pg. 19587
[55] See, EO 14072 at §1
[56] See, EO 14072 at §2
[57] See, Exec Order 14072; Vol. 87, No. 81 Federal Register 24852 (2022)
[58] See, Proposal at pg. 19588
[59] See, Executive Order No. 13563; Vol. 76 No 14 Fed Reg 3821; 2011 at§1(b)
[60] A complete copy of this memo is available here: Modernizing Regulatory Review | The White House
[61] See, DOI: CLIMATE ACTION PLAN 2021 Pg 3. A complete copy of this document is available here: Department of the Interior Climate Action Plan (doi.gov)
[62] See, USDA Forest Service; Organizations, Functions, and Procedures; Forest Service Functions; Advanced notice of rulemaking; request for comment; 88 Federal Register 24500 (April 21, 2023).
[63] See, 5 USC §552
[64] See, International Harvester Co. v. Ruckelshaus, 478 F.2d 615, 652 (D.C. Cir. 1973)
[65] See, Department of Commerce; Outdoor Recreation Satellite Account, U.S. and States, 2021 New statistics for 2021; 2017–2020 updated; Full release and tables pg. 5. A full copy of this report is available here: orsa1122.pdf (bea.gov)
[66] More information regarding this effort is available here: The BLM: A Sound Investment for America 2022. A copy of the BLM Sound investment 2022 report is attached as Exhibit “A” to these comments


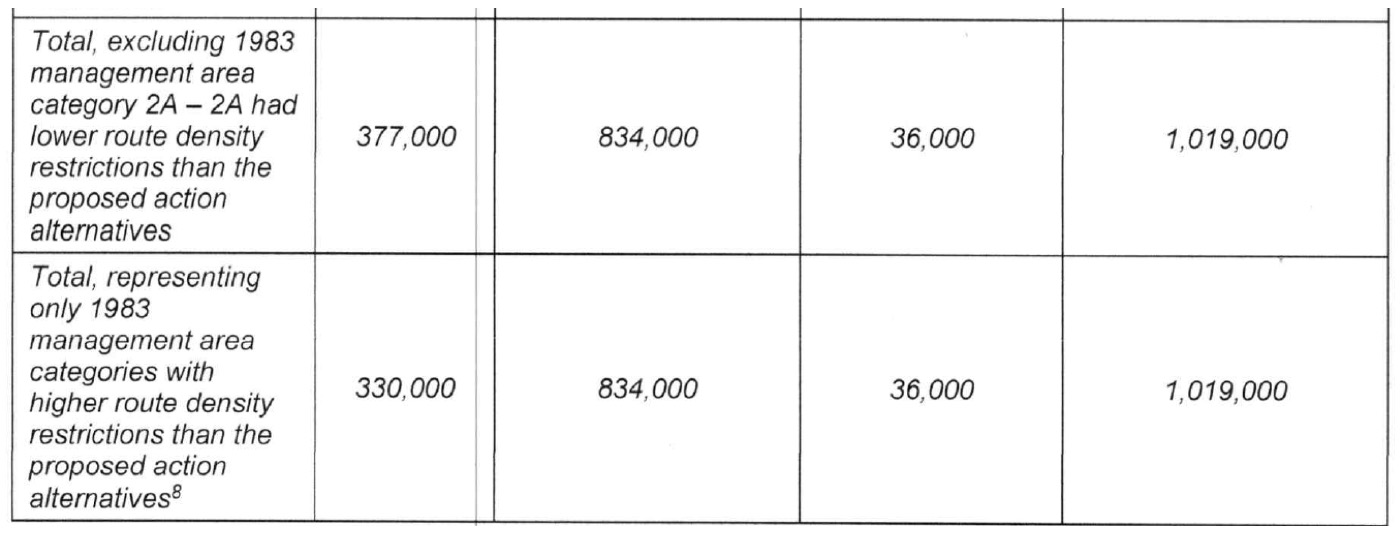
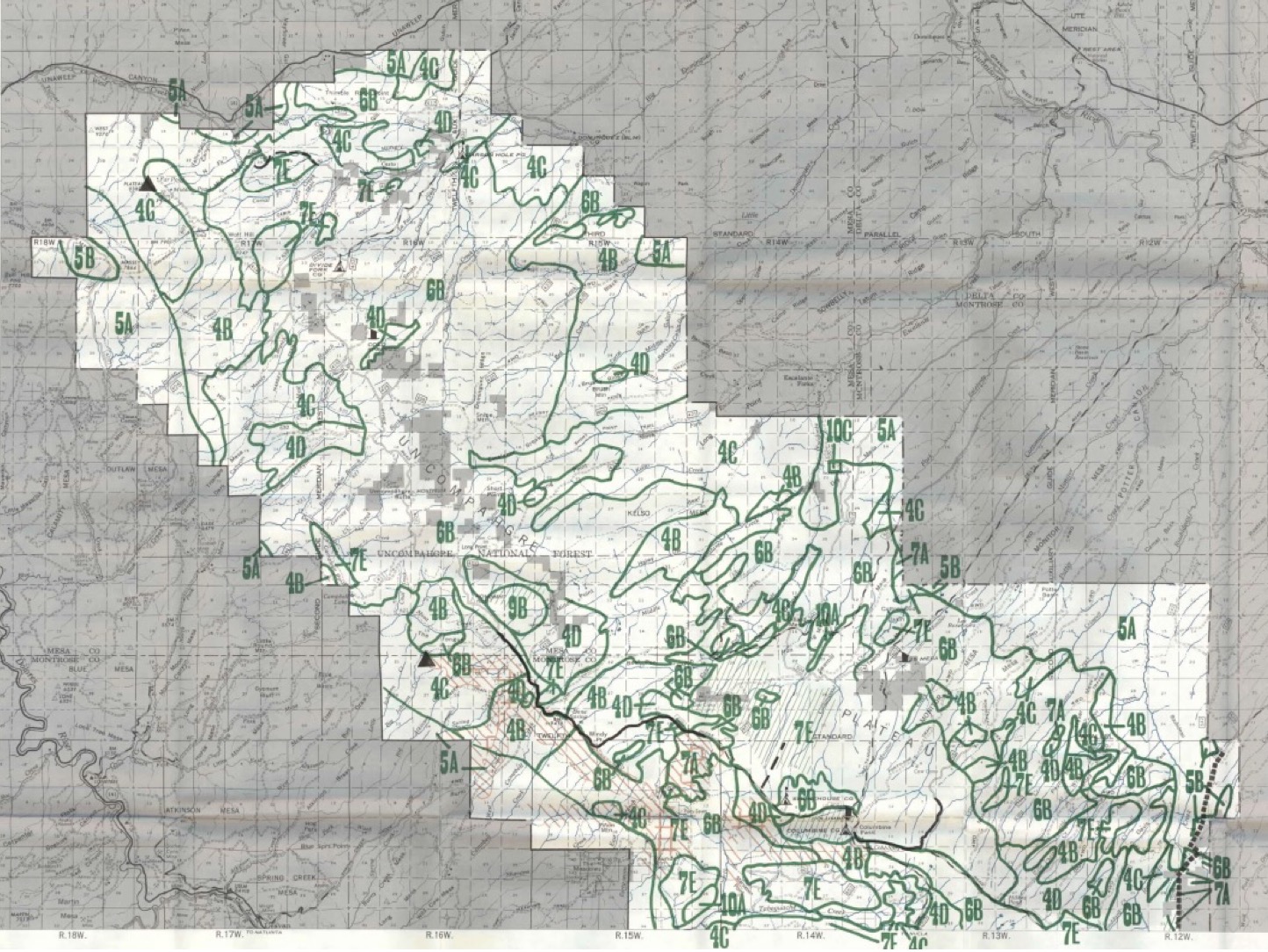
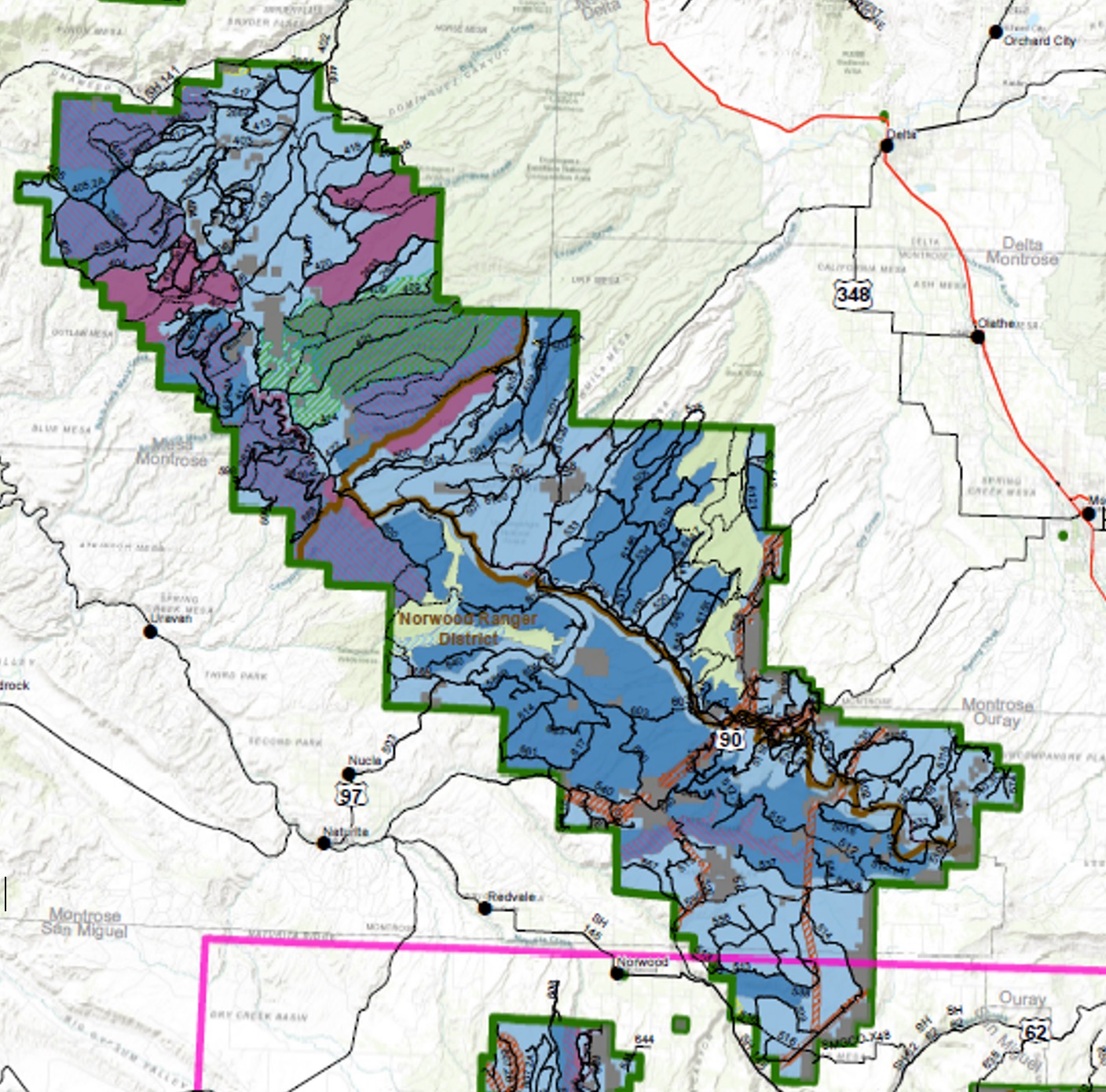















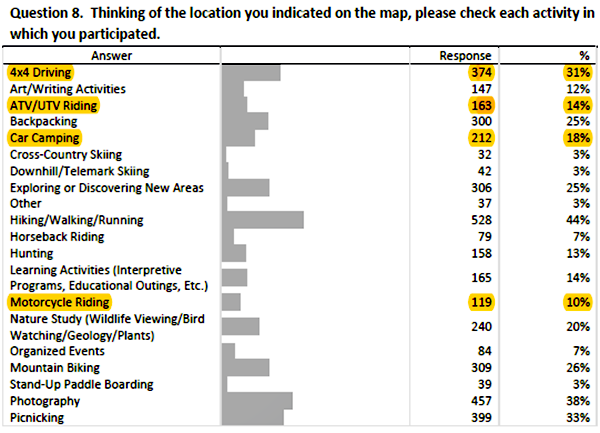
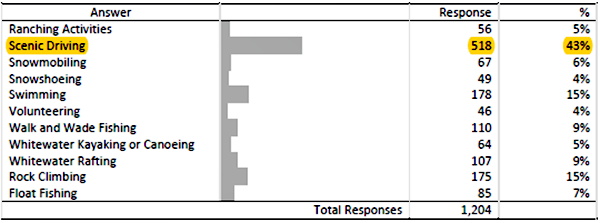











 Clive Heller has been unanimously voted in favor of being inducted as a TPA Board Member! Clive has been active in protecting and preserving Motorized Access in Colorado for far longer than most of us. Clive was one of the original members of the Colorado 600 Club long before there was a TPA. Clive has a tremendous perspective on motorized use on public lands and will be an excellent contributor on the TPA Board.
Clive Heller has been unanimously voted in favor of being inducted as a TPA Board Member! Clive has been active in protecting and preserving Motorized Access in Colorado for far longer than most of us. Clive was one of the original members of the Colorado 600 Club long before there was a TPA. Clive has a tremendous perspective on motorized use on public lands and will be an excellent contributor on the TPA Board.





 We are happy to announce that Scott Bright, who has been a part of the TPA Board of Directors since 2017 has been named Board President! Scott brings years of motorcycle industry and racing experience to the TPA. In addition, Scott is involved with numerous non-profit organizations, some of which he is the Chair.
We are happy to announce that Scott Bright, who has been a part of the TPA Board of Directors since 2017 has been named Board President! Scott brings years of motorcycle industry and racing experience to the TPA. In addition, Scott is involved with numerous non-profit organizations, some of which he is the Chair. 
